What is Zero Trust Security? Key Principles & Implementation
In a nutshell, Zero Trust Security is a modern approach to cybersecurity that operates on a simple but powerful principle: "never trust, always verify." It completely does away with the old-fashioned idea that anything inside your network is automatically safe. Instead, it treats every single attempt to access your data—no matter where it comes from—as a potential threat that needs to be rigorously checked.
A Deeper Look at the Zero Trust Security Model
Think about how security used to be handled. It was a lot like a medieval castle with a big wall and a deep moat. If you made it past the guards at the front gate, you were considered "trusted" and could pretty much wander wherever you wanted inside. This "castle-and-moat" security worked fine when all your employees and computers were physically inside the office building.

But today's workplace doesn't have walls. We have people working from home, apps running in the cloud, and personal smartphones connecting from all over the world. The concept of a secure "inside" of the network has vanished. The castle-and-moat strategy falls apart the second a hacker steals someone's login details and strolls right through the main entrance.
Zero Trust turns that entire idea upside down. Forget the castle. Imagine a top-secret government facility where you need to swipe your ID badge and prove your clearance at every single door. It doesn't matter if you were just in the office next door—to get into this new room, you have to prove who you are and that you're allowed to be there, every single time.
Shifting from Assumed Trust to Proven Identity
This radical change—from assuming trust to demanding proof—is the very heart of Zero Trust. It’s not a single piece of software you can install; it’s a strategic philosophy that changes how you think about and build your entire security system. It starts with the assumption that your network has already been breached and designs defenses to contain the damage.
The table below breaks down just how different this approach is.
| Security Aspect | Traditional Model ('Castle-and-Moat') | Zero Trust Model ('Never Trust, Always Verify') |
|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Trust everything inside the network perimeter. | Trust nothing. Verify every single request. |
| Access Control | Based on network location (inside vs. outside). | Based on user identity, device health, and context. |
| Verification | One-time check at the network entry point. | Continuous, real-time verification for every action. |
| Focus | Protecting the network perimeter from outsiders. | Protecting individual resources (data, apps) directly. |
| Assumption | The internal network is a "safe" zone. | Breaches are inevitable; assume the network is hostile. |
This model forces a shift from a static, one-time check to a dynamic, ongoing process of validation.
This constant verification is applied to absolutely everything: every user, every laptop, every application, and every piece of data. Before access is granted, each request is judged on factors like the user's identity, the security of their device, their location, and other real-time information. It’s a far more intelligent and granular way of doing things compared to the rigid, perimeter-focused security of the past.
The numbers show just how quickly businesses are making this shift. The global market for Zero Trust security was valued at USD 36.96 billion in 2024 and is expected to skyrocket to USD 92.42 billion by 2030. This incredible growth is driven by the realities of remote work, cloud computing, and the non-stop evolution of cyber threats.
This security philosophy doesn't just block external threats; it also builds stronger internal security habits. It perfectly complements the ideas we cover in our guide to document management best practices, where ensuring only the right people can access sensitive files is absolutely critical.
The Three Core Principles of Zero Trust
To really get what Zero Trust is all about, you have to look past the buzzword and understand the philosophy driving it. This entire approach is built on three core principles. They aren't just a checklist; they represent a fundamental shift in how we think about security, moving away from the old "castle-and-moat" model.
This diagram shows how these three pillars work together to form the foundation of a Zero Trust strategy.
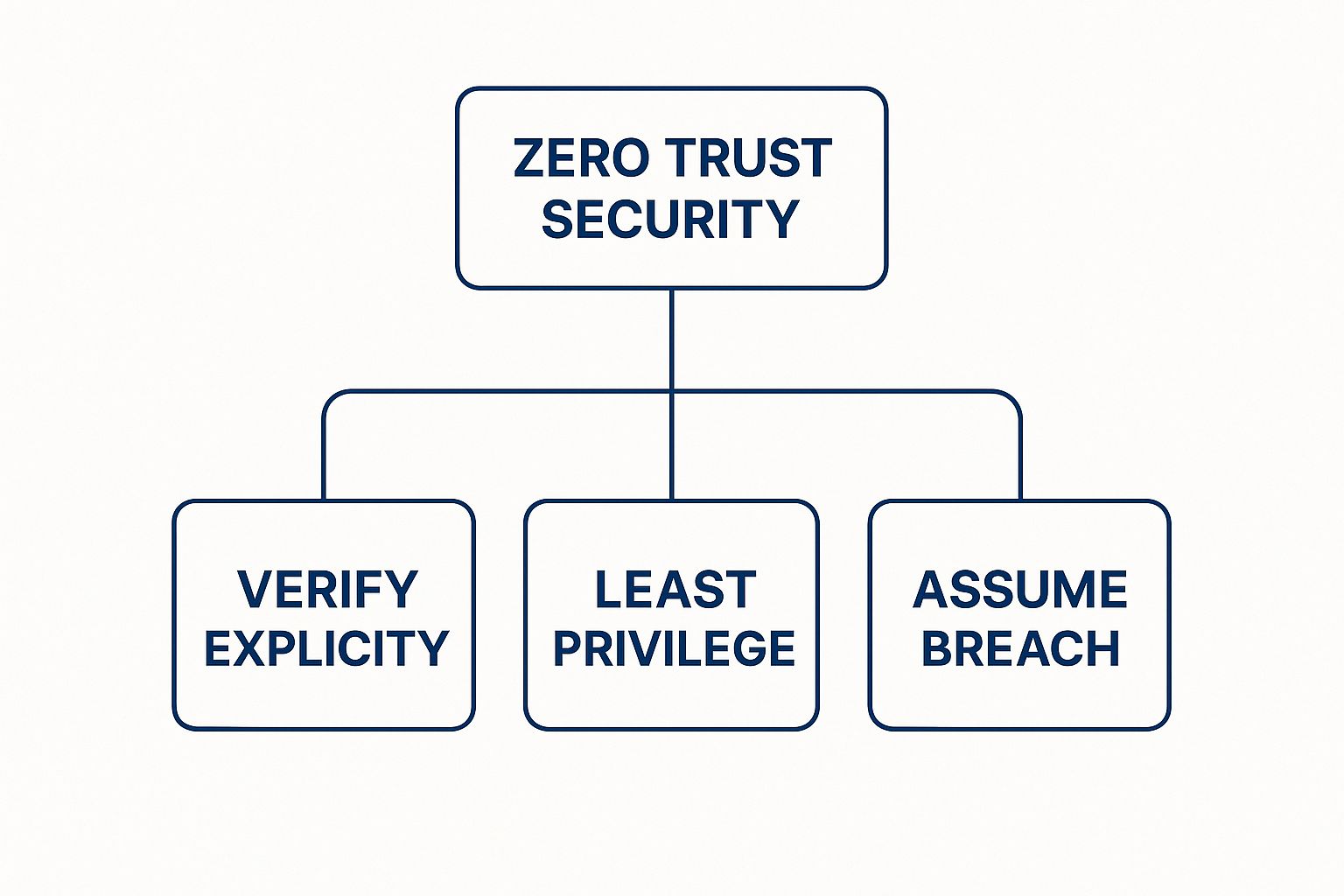
As you can see, these principles aren't isolated ideas. They're deeply connected, each one reinforcing the others to create a much more resilient and intelligent defense.
Principle 1: Verify Explicitly
The first and most well-known principle is to verify explicitly. This is where the motto "never trust, always verify" gets put into action. Think of it like a strict security checkpoint at a high-security building. The guard doesn't care if they just saw you five minutes ago; they're going to check your ID and credentials every single time you try to enter a new area.
In the digital world, this means every single request for access must be thoroughly authenticated and authorized. We're not just talking about a simple password, either. Verification should pull from every available signal to make an informed decision, including:
- The user's identity and their role in the company.
- The geographic location where the request is coming from.
- The security posture of the device being used (is it patched, is malware protection running?).
- The specific app, data, or service the user wants to access.
This constant, multi-faceted verification ensures trust is never implied just because someone is on the "right" network.
Principle 2: Use Least Privilege Access
Next up is the principle of least privilege access. Once a user or device is verified, they are only granted the bare-minimum permissions needed to do their specific job—and nothing more. This is a massive step in limiting the potential blast radius of any incident.
It’s like giving a plumber temporary access to just the basement of a building instead of handing over a master key to every room. The same logic should apply to your digital assets. Why would a sales associate need access to source code, or an HR manager need to see confidential legal discovery documents?
By rigorously applying the principle of least privilege, you dramatically shrink an attacker's opportunities. If an account is ever compromised, the intruder is stuck with only a tiny sliver of access, making it incredibly difficult for them to move laterally and cause widespread damage. This containment is a cornerstone of modern security and key to achieving data privacy compliance. For a closer look, you can explore our guide to navigating the complexities of data privacy compliance.
Principle 3: Assume Breach
Finally, the third principle is to assume breach. This is a powerful shift in mindset. It forces you to build your entire security system with the sobering assumption that an attacker is already inside your network.
Instead of focusing all your energy on building a taller wall, you also focus on making it impossible for an intruder to move around undetected once they're inside. This mindset directly leads to powerful security tactics like micro-segmentation, where the network is carved into small, isolated zones.
If a threat actor compromises one segment, they are effectively trapped. They can't jump to other parts of the network, which contains the threat and minimizes the damage. This "blast radius" limitation is absolutely critical in a world where breaches are not a matter of if, but when.
Key Technologies That Power a Zero Trust Architecture
The principles of Zero Trust tell us why we need it, but the technology is what makes it happen. A true Zero Trust architecture isn't a single product you can buy off the shelf. Instead, it's a carefully integrated system of tools that work together to enforce those core principles.
Think of it like a high-performance engine. Each component has a critical job, and the engine only hums when every part is working in perfect sync.

This synergy is what gives Zero Trust its power. It transforms your security from a collection of separate, siloed tools into a unified, intelligent defense system that can adapt to threats in real time.
The Gatekeeper: Identity and Access Management
At the very heart of this engine is Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM solutions are the central gatekeepers, maintaining a complete directory of every user and device trying to connect. It’s the brain of the operation, deciding who is who and what they are allowed to see and do.
An IAM system is responsible for the entire lifecycle of a user's identity—from creation to deletion. More importantly, it enforces access policies based on roles, ensuring an accountant can’t poke around in engineering files and vice versa. It’s the solid foundation upon which every other Zero Trust technology is built.
The Double-Check: Multi-Factor Authentication
If IAM is the gatekeeper, then Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is the mandatory double-check at the gate. Passwords alone are a thing of the past; relying on them is like locking your front door but leaving the key under the welcome mat. MFA forces users to prove their identity with two or more verification factors before they get access.
This approach is quickly becoming the norm. A Gartner survey predicts that by 2025, 63% of organizations will have implemented a Zero Trust strategy, with this kind of continuous identity check as the first line of defense. Because passwords can be stolen, methods like biometrics, security tokens, or one-time codes sent to a trusted phone are essential. Robust authentication is a non-negotiable cornerstone of Zero Trust, and tools like Duo Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are prime examples of this principle in action.
The Fire Doors: Micro-segmentation
Once a user is verified and inside, their movement must be tightly controlled. This is where micro-segmentation comes in. Imagine your network is a large building. Instead of one big, open-plan office, micro-segmentation installs secure, automatically locking fire doors between every single room and corridor.
This practice carves the network up into tiny, isolated security zones. If an attacker somehow compromises one segment—say, a single development server—they are trapped. They can’t move laterally to other parts of the network, which effectively contains the breach and drastically limits the potential damage. This is how the "Assume Breach" principle is brought to life.
Key Takeaway: The goal of micro-segmentation is to shrink the "blast radius" of an attack. By containing threats to a small, isolated area, you prevent a minor incident from becoming a catastrophic, company-wide breach.
This granular level of control is a core part of a mature security posture. You can see how these advanced controls fit into a wider strategy by reading our guide on https://www.whisperit.ai/blog/data-security-best-practices.
The Health Check: Endpoint Security
Finally, every device connecting to your network is a potential entry point. Endpoint Security ensures that every single laptop, server, and smartphone is healthy and compliant before it’s allowed to connect. Think of it as a personal health inspector for each device.
These tools run a constant health check, looking for things like:
- Updated Antivirus: Is the device running up-to-date malware protection?
- Patch Status: Are the operating system and all apps patched against the latest known vulnerabilities?
- Configuration: Does the device's setup meet the company's security standards?
If a device fails this health check, it’s simply denied access until the issues are fixed. This is a simple but powerful way to prevent compromised or vulnerable endpoints from ever introducing threats into your secure environment.
Why Zero Trust Is Essential in High-Stakes Industries
In some industries, a single data breach isn't just a problem; it's a catastrophe. For fields built on sensitive information, the "never trust, always verify" mindset of Zero Trust shifts from a security buzzword to a fundamental operational requirement.

Think about healthcare. Hospitals and clinics are custodians of Protected Health Information (PHI), which is not only incredibly valuable to criminals but also strictly regulated. A traditional security setup might give a doctor wide-ranging network access once they’re logged in. But what happens if their credentials fall into the wrong hands?
Securing Healthcare with Granular Controls
A Zero Trust model completely flips that script. It doesn't automatically trust a user just because they're on the "right" network. Instead, it scrutinizes the context of every single action.
Let's imagine a cardiologist trying to open a patient's chart. The Zero Trust system does more than just ask for a password. It asks a series of questions:
- Is this really the right doctor? It confirms with multi-factor authentication.
- Is the device they're using secure and up-to-date? An endpoint health check provides the answer.
- Does this doctor have explicit, pre-approved permission to view this specific patient's cardiac records? This is the principle of least privilege in action.
Now, what if that same cardiologist tries to peek at dermatology records for a completely different patient? The request is instantly blocked. This level of granular control is crucial for maintaining HIPAA compliance and preventing data exposure, whether it's accidental or malicious. Even if an attacker gets in, they are trapped and can't move laterally to steal other patient data. This kind of thinking is a core part of any meaningful security risk assessment.
Protecting Client Confidentiality in the Legal Field
The entire legal profession is built on a bedrock of trust and confidentiality. For a law firm, information is everything—client communications, case strategies, privileged documents. A breach doesn't just cost money; it can shatter a firm's reputation and irrevocably break attorney-client privilege.
Zero Trust offers the robust safeguards needed in this environment. It protects sensitive case files by using micro-segmentation, which essentially builds secure digital walls between different cases or practice areas. An attorney working on a major corporate merger would have absolutely no visibility into the files for an intellectual property lawsuit happening down the hall.
By verifying every single access attempt, Zero Trust neutralizes threats from both sophisticated external hackers and potential insider risks. It guarantees that only the specifically assigned legal team can touch a client’s documents, locking down confidentiality at every turn.
This approach is central to effective modern data breach prevention across the board. By starting from a position of zero implicit trust, the framework creates a resilient defense that is purpose-built to protect the most sensitive data right where it lives. For high-stakes sectors, it's not just an option—it's the only responsible way forward.
Your Roadmap to Implementing a Zero Trust Strategy
Thinking about Zero Trust as a flip you can switch overnight is a common mistake. It's really a journey—a fundamental rethinking of your entire security philosophy. You're moving away from the old idea of a secure "inside" and a dangerous "outside" and embracing a model that trusts no one by default. The best way to manage this transition is with a clear, phased roadmap.
It all starts with one simple question: What are you actually trying to protect? You can't secure what you can't see. The first real step is to pinpoint your most critical assets—the sensitive data, vital applications, and core services that your organization can't function without. Once you know what they are, you need to map out exactly how information moves, who needs access to it, and from where. This discovery work is essential; it gives you the blueprint for building your defenses.
Phase 1: Laying the Foundation
With a clear map in hand, it's time to pour the concrete. This phase is all about putting the foundational security controls in place that will support everything else. Two elements are absolutely non-negotiable here:
- Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM): You need a single, authoritative system that manages and verifies every single user and device. This becomes your trusted source for confirming identities.
- Universal Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Roll out MFA for everyone, everywhere. No exceptions. This is one of the single most powerful steps you can take to shut down attacks that rely on stolen passwords.
These two controls directly enforce the core "Verify Explicitly" principle, making sure every attempt to access your resources starts with a proven, legitimate identity. This stage is also the perfect time to run a full analysis of your vulnerabilities. For a step-by-step guide, check out our post on how to conduct a risk assessment.
Phase 2: Maturing Your Security Posture
Once your foundation is solid, you can start building up. This next phase is about maturing your security capabilities and fully embracing the principles of least privilege and "Assume Breach." A key move here is deploying micro-segmentation. Think of it as creating secure, isolated rooms within your network. If a threat gets into one room, micro-segmentation keeps it from spreading to others.
Another critical piece is setting up continuous automated monitoring. This isn't just about logging events; it's about actively analyzing signals from your entire environment to spot strange behavior and react to threats the moment they appear.
A Note on Challenges: Let's be realistic—the road to Zero Trust has its bumps. Many organizations run into challenges like finding enough skilled cybersecurity talent, dealing with the cost of integrating new tools with old systems, and worrying about getting locked into a single vendor's ecosystem. These are real concerns that require smart planning and dedicated investment.
Beyond the technology, a successful Zero Trust program depends on your people. It demands a culture shift where everyone, from the C-suite to the newest hire, understands their role in security. That's why fostering a culture of security is just as crucial as any software you install. By tackling this journey in manageable phases, you can build a truly resilient security framework that protects your organization from modern threats.
Answering Your Questions About Zero Trust
Whenever there's a big shift in how we approach security, questions—and a few myths—are sure to follow. Getting straight answers about Zero Trust is the best way to see its real-world value and move forward with a clear plan. Let's tackle some of the most common ones.
The biggest misconception? That Zero Trust is a single product you can just buy and install. It’s not. It’s much more like a detailed architectural blueprint for your entire security setup. Think of it as a guiding philosophy and strategic framework, not a plug-and-play device.
A successful Zero Trust environment is built by weaving together different technologies—like Identity and Access Management (IAM), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and endpoint security. All these pieces work in concert to enforce that core principle of “never trust, always verify” everywhere.
Will Implementing Zero Trust Slow Everything Down?
This is a huge concern for many people. If we’re adding more security checkpoints, won't that create frustrating bottlenecks for our users? The short answer is: not if it's done right.
While it’s true that Zero Trust introduces more verification steps, modern tools are designed to be incredibly efficient. A well-planned rollout can actually speed things up by optimizing traffic and routing requests more intelligently.
If you do see slowdowns, it's almost always an issue with the implementation, not a fundamental flaw in the Zero Trust model itself. The real goal is to make security so seamless that it’s nearly invisible to the end user.
Key Insight: A well-executed Zero Trust strategy boosts security without hurting productivity. The focus is on continuous verification that works behind the scenes, protecting your data without getting in the way.
Can Small Businesses Realistically Implement This Model?
Absolutely. The idea that Zero Trust is only for giant corporations is a complete myth. The model is flexible and scales to fit businesses of any size. In fact, many cloud services now offer core Zero Trust features like MFA and identity management at a price point that makes them accessible to everyone.
A small business doesn't have to boil the ocean. You can take it one step at a time, starting with the changes that give you the biggest security bang for your buck. For instance:
- Start with Identity: Your first and most powerful move is enforcing strong multi-factor authentication for everyone, across every app.
- Secure Key Data: Figure out what your most critical data is and lock it down first with tight, granular access controls.
- Grow Gradually: As your business evolves, you can layer on more advanced capabilities like device health checks or micro-segmentation.
The path to Zero Trust is a marathon, not a sprint. By taking a phased approach, even the smallest business can build a powerful, modern security posture that stands up to today’s threats.
For professionals in legal and healthcare, protecting sensitive information is non-negotiable. Whisperit is built on a foundation of security, ensuring your dictated and transcribed documents are protected with Swiss hosting, end-to-end encryption, and compliance with GDPR and SOC 2 standards. See how we can secure your workflow at https://whisperit.ai.