Voice Recognition Software Medical: Improve Clinical Documentation
At its core, medical voice recognition software is a specialized tool that listens to a clinician's spoken notes and instantly converts them into written text, right inside a patient's electronic health record (EHR). Think of it as a highly intelligent digital scribe, working tirelessly to free doctors, nurses, and other providers from the keyboard.
This frees up an incredible amount of time, shifting the focus from tedious data entry back to where it belongs: on the patient.
The End of Endless Clinical Paperwork
Picture a typical clinic. How much of a doctor's day is spent face-to-face with patients versus head-down, typing into a computer? The reality is often staggering. Many studies have shown that for every one hour of direct patient contact, physicians can spend up to two hours on administrative desk work.
This mountain of paperwork isn't just an inconvenience; it's a primary driver of clinician burnout. The constant pressure to document everything perfectly is exhausting, and it's taking a toll on healthcare professionals and the quality of care they can provide.

This is where voice recognition software medical solutions are making a real difference. It’s like having an expert medical scribe on call 24/7 who is fluent in every specialty, from cardiology to orthopedics. The technology listens, understands the complex language of medicine, and captures the details of each clinical encounter—turning spoken words into structured, compliant documentation in real-time.
Why This Technology Matters Now
With the widespread adoption of EHRs and a greater focus on value-based care, detailed documentation is more important than ever. But the manual way of doing things is slow, frustrating, and often leads to errors. Medical voice recognition directly tackles these challenges.
- It Gives Time Back: Most clinicians can speak their notes up to three times faster than they can type them. This simple change can reclaim hours every single week.
- It Boosts Note Quality: The best systems are trained on vast medical vocabularies, ensuring that clinical notes are captured with precision and detail. For more on this, check out our medical documentation guidelines.
- It Improves Provider Well-being: By lifting a huge administrative weight, this software helps reduce stress and burnout, allowing clinicians to reconnect with why they got into medicine in the first place.
This technology is more than a productivity tool; it’s a strategic asset for modern healthcare organizations. It directly impacts the triple aim of improving patient experience, enhancing population health, and reducing the per capita cost of care.
In this guide, we'll walk you through how this technology works, explore the real-world benefits across different specialties, and cover what you need to know to bring it into your practice successfully. You'll soon see how voice recognition software medical systems are not just changing how notes are written but are fundamentally improving the practice of medicine.
How Voice AI Actually Understands Medical Language
It can feel a bit like magic when you speak into a microphone and a perfect clinical note appears moments later. But what's really going on behind the scenes? It's not magic, but a sophisticated tag team of two different AI technologies working together to turn spoken words into structured, usable clinical data.
First up is Automated Speech Recognition (ASR). Think of ASR as the ears of the operation. Its only job is to listen carefully to a clinician’s voice—catching every word, inflection, and pause—and convert that audio into a simple block of text. This first step is crucial, as it lays the groundwork for everything that follows.
But a raw transcript isn't very helpful in a clinical setting. It might have the right medical terms, but it's just a jumble of words without any context, structure, or medical meaning. That’s where the second, more advanced AI steps in to make sense of it all.
The Brains of the Operation: Natural Language Processing
If ASR is the ears, then Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the brain. Picture an expert medical scribe who doesn't just hear what's being said but instantly grasps its clinical significance. That’s exactly what NLP does. It takes the raw text from the ASR, analyzes it, and starts pulling out the key medical concepts to build a coherent note.
These specialized NLP models are trained on gigantic datasets—think medical textbooks, de-identified patient charts, and millions of clinical documents. This deep training gives the software the ability to:
- Grasp Complex Terminology: It knows the critical difference between "hypotension" and "hypertension" and can correctly identify specific drug names and procedures from dictation.
- Pinpoint Clinical Details: The system can pick out diagnoses, symptoms, lab results, and treatment plans from a natural conversation.
- Structure the Story: NLP is smart enough to take dictated information and put it in the right place, sorting everything into sections like History of Present Illness (HPI), Physical Exam, or Assessment and Plan.
This simple flow chart shows how it all comes together, from the doctor's voice to the final note in the patient record.
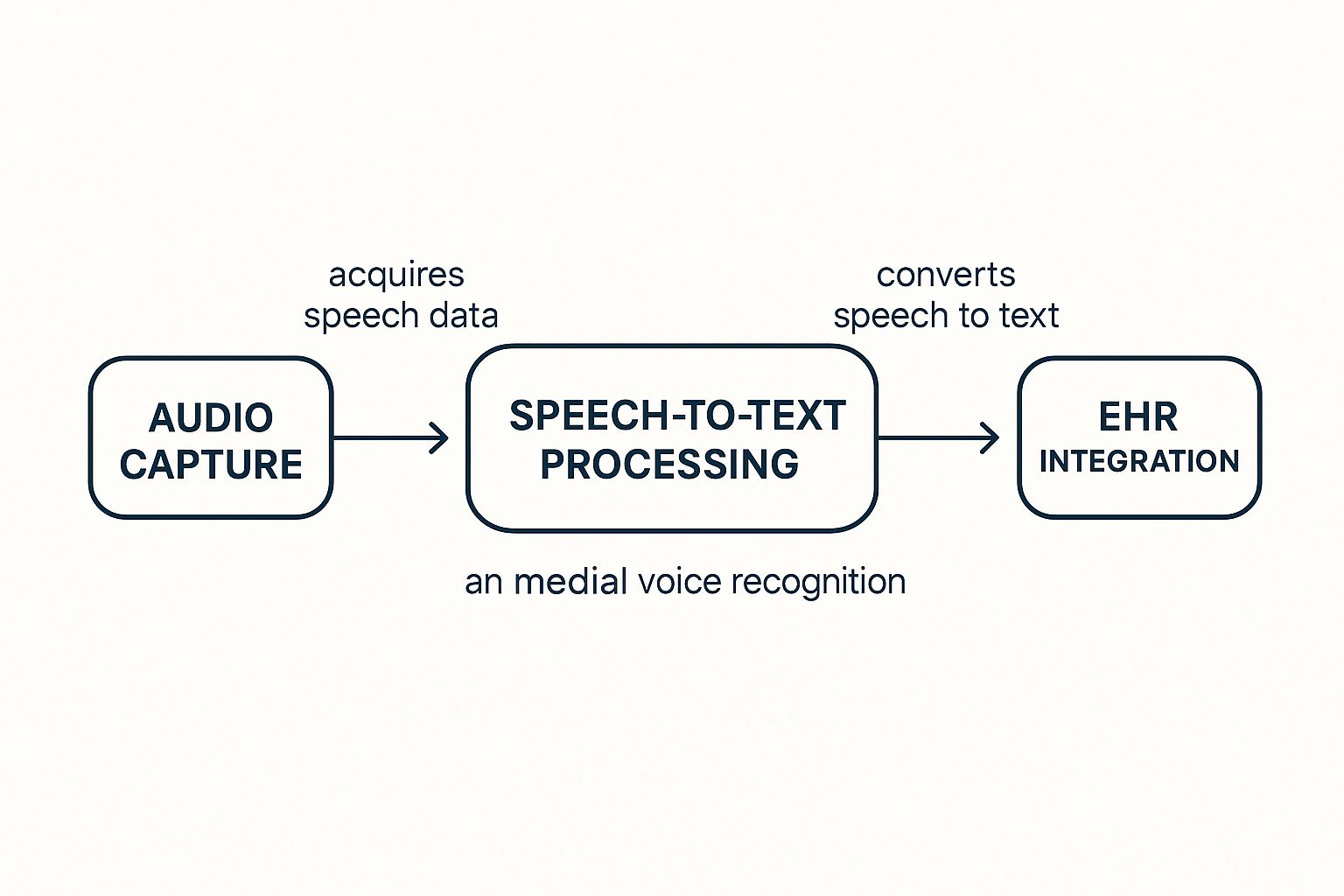
As you can see, it's a seamless journey where spoken audio is first turned into text, then intelligently organized and slotted right into the patient’s chart.
Training AI to Be Medically Fluent
Getting this right is incredibly difficult. Medicine is packed with jargon, acronyms, and subtle phrasing that would trip up a standard voice assistant in a heartbeat. To handle this, medical voice recognition software goes through some seriously intense training.
These AI models are constantly refined on millions of hours of real-world medical dictations from every specialty imaginable, from cardiology to pediatrics. This process teaches the system to understand different accents, speaking paces, and the unique vocabulary that comes with each medical field. The end result is a system that isn't just hearing words—it's truly understanding them.
You can think of ASR and NLP working like a highly efficient physician-scribe duo. The ASR diligently captures every word spoken, and the NLP then interprets, structures, and files that information neatly into the EHR. It creates a complete, accurate record without anyone having to lift a finger to type.
This powerful combination makes documentation not just faster, but far more detailed and clinically accurate. For any practice looking to get the most out of this technology, these clinical documentation improvement tips can help take your records to the next level. Ultimately, the system transforms a simple conversation into a valuable data asset, ready for immediate clinical use.
Unlocking Key Benefits in Clinical Practice
Knowing how medical voice recognition works is one thing, but seeing how it actually changes the day-to-day grind in a clinic is where the real value becomes clear. The perks go way beyond just being a neat convenience; they touch on the very core of healthcare—efficiency, accuracy, and even the well-being of the providers themselves.
At the most basic level, voice recognition software is just faster. Plain and simple. Most clinicians can talk a lot faster than they can type, with some studies showing dictation can be up to three times quicker. This speed directly translates into reclaimed time, letting doctors move between appointments more smoothly and knock out their notes without the usual delay.
Think about it: instead of spending an extra hour after the last patient, painstakingly typing out records, a provider can just dictate the key findings and plan in a few minutes. That immediate time-saving is often the first and most tangible benefit practices notice.

Driving Greater Documentation Efficiency
The efficiency gains are about more than just raw speed. The best medical voice recognition tools plug right into your existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. This means the transcribed text lands exactly where it needs to go in the patient's chart, killing the clumsy process of copying, pasting, and flipping between windows.
This direct integration turns a clinician's voice into structured reports and treatment plans, slashing the time spent on manual entry. We're not talking about a small improvement, either. Research shows that modern automated speech recognition (ASR) can hit over 90% accuracy on medical dictations. For example, people using systems like Nuance's Dragon Medical One often report finishing their notes 30-50% faster than when they were typing.
Enhancing Clinical Accuracy and Detail
Speed is great, but it’s useless without accuracy. This is where specialized medical vocabularies make all the difference. These aren’t your average consumer dictation tools; medical-grade software has been trained on millions of clinical terms, drug names, and procedural jargon.
This training ensures that when a cardiologist says "systolic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction," the system gets it right, instead of spitting out something that sounds similar but is clinically meaningless. That kind of precision is absolutely critical for patient safety, proper billing, and making sure the next provider knows exactly what's going on.
By capturing a clinician's exact words in the moment, voice recognition often creates notes that are far more detailed and nuanced than typed ones. This builds a richer, more complete patient story that’s invaluable for future appointments and coordinating care.
Creating such specific and accurate notes is fundamental to good medicine. If you're looking for ways to elevate your practice's record-keeping, our guide on improving clinical documentation offers practical strategies to make sure every important detail is captured correctly.
Combating Clinician Burnout
This might be the most important benefit of all: the impact on clinician well-being. The crushing administrative burden of documentation is a huge contributor to physician burnout, a crisis that's hitting healthcare systems everywhere. By taking a huge chunk of that work off their plate, voice recognition software medical solutions give providers their time back.
And what they do with that time is what truly matters:
- More Face-to-Face Patient Interaction: Clinicians can look at their patients instead of a screen, which builds stronger relationships and leads to better communication.
- Reduced "Pajama Time": This is the industry term for doctors taking work home. Good software helps end that, allowing for a much healthier work-life balance.
- Renewed Professional Satisfaction: Take away one of the biggest daily frustrations, and you let clinicians get back to the parts of medicine they actually love. This leads to higher job satisfaction and helps keep good people in the profession.
Ultimately, these benefits create a virtuous cycle. Better documentation leads to better patient care, and less administrative stress creates a more sustainable and fulfilling environment for the healthcare professionals we all depend on.
Real-World Applications Across Medical Specialties
The best way to grasp the power of medical voice recognition software is to see how it works in the real world, fundamentally changing the day-to-day for clinicians in different fields. This isn't just some generic, off-the-shelf tool. It's a highly adaptable partner that flexes to meet the unique needs of each medical specialty. From the chaotic pace of an emergency room to the intense focus of a radiology reading room, its impact is both significant and personal.
Take a radiologist, Dr. Anya Sharma, who is analyzing a complex CT scan of a patient's abdomen. Her eyes are glued to the screen, searching for subtle signs that could point to a serious condition. Instead of breaking her concentration to type or fiddle with a clunky foot pedal, she simply speaks into a microphone, dictating her findings as they happen.
"The liver shows diffuse heterogeneity with multiple hypodense lesions consistent with metastatic disease," she says clearly. "The largest lesion in the right hepatic lobe measures 3.2 centimeters." The software instantly converts her specialized medical language into a perfectly structured report. This seamless flow means she never has to look away from the images, ensuring no critical detail slips through the cracks.
Streamlining Patient Encounters in Primary Care
Now, let's step into the office of Dr. Ben Carter, a primary care physician. He’s using an ambient clinical intelligence tool, which is a more advanced form of voice recognition that listens quietly in the background during appointments. As he and his patient discuss managing type 2 diabetes, the software captures their entire conversation.
It’s smart enough to tell the difference between Dr. Carter's questions and the patient's answers, pulling out the important clinical details. When the patient mentions a new tingling in their feet, the AI notes it as a possible sign of neuropathy. Before the visit is even over, a draft note is waiting in the EHR—complete with the patient's history, new symptoms, and the treatment plan Dr. Carter discussed. All he needs to do is a quick review and sign-off, saving him 10-15 minutes of charting for every single patient.
This ambient listening doesn't just save time; it transforms the entire patient-provider dynamic. Dr. Carter can maintain eye contact and truly listen, building a stronger connection without a computer screen acting as a barrier. It brings the focus back to human-centered care.
This is a game-changer for specialties where the patient's story is the most important piece of the puzzle. As voice AI becomes more common, it's also making documentation easier for remote care, including for complex evaluations like telehealth autism diagnoses.
Ensuring Precision in the Operating Room
Finally, picture Dr. Lena Petrova, a surgeon who just finished a complex knee replacement. She’s still in the sterile OR and needs to document the procedure while every detail is crystal clear. Taking off her gloves to type on a keyboard is out of the question.
Instead, she dictates her post-operative note completely hands-free. "Procedure: total knee arthroplasty, right. Implant: Zimmer Persona, size 5 femoral, size 4 tibial..." she states. The software captures it all, from the specific implant models to the estimated blood loss. This immediate dictation guarantees accuracy and gives the recovery team in the PACU instant access to the most current information.
Comparison of Medical Voice Recognition Software Features
When you're ready to explore different options, it helps to know what to look for. Not all systems are created equal, and the right features can make all the difference for your specific workflow.
This table breaks down some of the most important features to consider.
| Feature | Description | Importance in a Medical Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Vocabulary | The software's built-in dictionary of medical terms, drug names, and specialty-specific jargon. | Critical. A robust vocabulary ensures high accuracy and minimizes the need for corrections, especially in complex fields. |
| EHR Integration | The ability to connect directly with your Electronic Health Record system to populate notes and data. | Very High. Seamless integration saves time by eliminating the need to copy and paste, reducing the risk of errors. |
| Ambient Listening | The system actively listens to conversations in the background and drafts clinical notes automatically. | High. This is a major time-saver in primary care and specialties that are conversation-heavy. |
| Mobile Accessibility | The ability to dictate notes using a smartphone or tablet, whether in the clinic or on the go. | High. Provides flexibility for clinicians who move between different locations or need to document outside of office hours. |
| Customization & Templates | Allows users to create custom commands, templates, and shortcuts for frequently used phrases or notes. | Medium. Greatly improves efficiency for repetitive documentation tasks and personalizes the workflow. |
| HIPAA Compliance | Adherence to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act to protect patient data. | Non-negotiable. The software must have strong security and privacy measures to be used in any clinical setting. |
Choosing the right software involves matching these features to the unique demands of your practice.
These scenarios just scratch the surface of the software's versatility. It's not a rigid, one-size-fits-all product but a flexible platform that delivers real, tangible benefits to medical professionals in any role. Whether it's helping a doctor focus on a diagnosis, fostering better communication with patients, or keeping the operating room sterile, medical voice recognition software is reshaping how healthcare is delivered. To get a better sense of the core technology, our guide on medical speech-to-text software offers a closer look at how these systems work.
Navigating HIPAA Compliance and Data Security
In healthcare, patient information isn't just sensitive—it's legally protected. So when you're looking at any new technology that handles patient conversations, the first and most important question has to be about security. With voice recognition software medical solutions, meeting the standards of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) isn't just a nice-to-have feature. It’s the entire foundation.
Any note, diagnosis, or treatment plan spoken aloud and captured by the software instantly becomes Protected Health Information (PHI). That PHI has to be shielded from prying eyes at all times. This is exactly why the leading voice recognition platforms are built from the ground up with multiple layers of security designed specifically for the rigors of a clinical environment.
Think of it as a digital armored car. The second a doctor speaks, that voice data is encrypted, sent securely to a protected server for processing, and then slotted right back into the EHR. The raw information is never left exposed.

Core Security Features to Demand
When you're vetting a potential vendor, you need to push past the polished demos and ask some hard-hitting questions about their security. A truly compliant solution will have a very specific set of safeguards that are simply non-negotiable.
Here are the absolute must-haves for your checklist:
- End-to-End Encryption: All data, whether it's voice or text, must be encrypted while it's moving across your network (in transit) and while it's being stored on servers (at rest). If anyone ever managed to intercept it, the data would be completely unreadable.
- Secure Cloud Environments: The vendor has to use a HIPAA-compliant cloud setup. This could be a private cloud or a secure, dedicated space with a major provider like AWS or Microsoft Azure.
- Granular Access Controls: Not everyone on your team needs to see every piece of patient data. Good software lets you set role-based permissions, so clinicians only have access to the information they absolutely need to do their jobs.
These technical pillars are what make a system truly secure, turning what could be a massive compliance headache into a simple, clear-cut evaluation.
The Non-Negotiable Business Associate Agreement
Beyond the tech, there's a critical legal document you can't ignore: the Business Associate Agreement (BAA). This is a formal, legally binding contract between your practice (the Covered Entity) and the software company (the Business Associate) that will be handling PHI for you.
This document clearly spells out the vendor's responsibilities for protecting patient data and confirms they will uphold all the safeguards HIPAA demands. If a vendor can’t—or won’t—sign a BAA, that’s an immediate dealbreaker. It's the biggest red flag you can get.
A Business Associate Agreement is not just a piece of paper. It’s the legal guarantee that your tech partner is just as committed to patient privacy as you are, and that they share the liability if something goes wrong.
Figuring out the ins and outs of data security is a huge part of running a modern practice. For a more detailed guide, you can walk through our HIPAA compliance requirements checklist. In the end, choosing a voice recognition software medical solution with a strong, transparent security framework gives everyone—from your staff to your patients—peace of mind, ensuring this powerful tool only ever enhances care without putting privacy at risk.
A Practical Roadmap for a Smooth Rollout
Bringing voice recognition software into a clinical setting isn't just an IT project—it's a fundamental shift in how your clinicians work. To get it right, you need a solid plan that puts your doctors and nurses first, guiding your organization from the initial idea to full-scale adoption with as few headaches as possible.
The journey always starts with a thorough needs assessment. Don't guess what your clinicians need; go out and ask them. Pinpoint the biggest documentation bottlenecks in different departments. Maybe your ER team is struggling with slow note turnaround, while your family practice doctors are getting buried in paperwork from long patient histories. Nailing down these specific pain points helps you set clear, realistic goals for what you want to achieve.
Building Your Foundation for Success
Once you know what you're solving for, you can start looking at vendors. Find a partner who truly understands healthcare and offers a solution that plays nice with your current EHR. Nothing kills a new tool faster than a clunky integration that adds more clicks and friction to a provider's day. The right vendor should feel like a part of your team, not just a software seller.
A successful rollout is built on a foundation of clinician enthusiasm. The goal isn't just to install software; it's to introduce a tool that providers genuinely want to use because it makes their lives easier and improves their ability to care for patients.
Next, kick things off with a pilot program. Handpick a small group of tech-savvy, enthusiastic early adopters from various departments. These champions will be your test pilots, working out the kinks, fine-tuning workflows, and giving you the honest feedback you need. Their success stories will be your most powerful tool for getting everyone else on board.
Driving Adoption Through Smart Training and Customization
Great training is absolutely critical. A generic webinar just won't cut it. You need to provide hands-on, role-specific sessions that show clinicians exactly how to weave the software into their day-to-day work. Focus on real-world skills, like mastering voice commands, creating shortcuts for common visit types, and adding personal terms to their medical dictionaries.
The demand for these tools is exploding for a reason. The global medical speech recognition market was valued at USD 1.73 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit USD 5.58 billion by 2035. This surge is driven by major players like Northwestern Medicine, which is using ambient voice AI to automatically convert patient conversations into ready-to-sign clinical notes. You can explore more about these market trends and their drivers to see where the industry is headed.
For the long haul, customization is king. Work with each department to build voice-activated templates for their most common diagnoses and procedures. Think about it: when a radiologist can dictate a perfectly structured MRI report with a single voice command, you've gone way beyond simple dictation. You've unlocked real efficiency. That’s how a useful tool becomes an indispensable part of their practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
It's only natural to have questions when you're looking at bringing new technology into your practice. When it comes to something as central as clinical documentation, you need straightforward answers. Let's tackle some of the most common questions we hear from clinicians and administrators.
How Accurate Is This Software, Really?
I get this question all the time, and for good reason. The short answer is: modern medical voice recognition is incredibly accurate. We're talking over 95% accuracy right from the start, mainly because these systems are pre-trained on massive medical vocabularies specific to different specialties.
But accuracy isn't just about the software; it's a partnership. A few things can make a huge difference:
- Your Microphone: A high-quality, noise-canceling microphone is non-negotiable. It’s the single biggest factor in getting clean, accurate transcriptions.
- Your Environment: Dictating in a quiet office will always beat trying to do it in a bustling hospital hallway.
- A Little Patience: The software actually learns your voice—your unique accent, cadence, and speech patterns. The more you use it, the smarter it gets.
What Are the Biggest Hurdles with EHR Integration?
Let's be honest, integrating any new tool with an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system can be a headache. The biggest challenge with voice recognition software is making it feel like it belongs there. If your team has to constantly jump between windows or copy-paste text, they’ll abandon it in a heartbeat.
The best voice recognition tools are built to embed directly into major EHR platforms like Epic, Cerner, and Athenahealth. This is key. It means you can dictate straight into the patient chart, exactly where the text needs to go. Before you sign any contract, make sure the vendor can demonstrate a truly seamless integration with your specific EHR.
What’s the Real Cost and Is It Worth It?
Most medical voice recognition software is sold as a subscription, usually on a per-user, per-month basis. While it is a new line item in your budget, the return on investment (ROI) comes from getting your time back.
Think about it: when a physician saves even 30-60 minutes a day on paperwork, that's time that can be spent with more patients. That directly impacts the bottom line and, just as importantly, helps chip away at clinician burnout.
The demand for these tools is exploding. EHR adoption has skyrocketed to 97.4% in U.S. hospitals, creating a huge need for anything that makes them easier to use. That’s why global investment in voice technology hit USD 2.5 billion in 2024, with roughly a third of health systems now trying out advanced ambient documentation tools. You can read more about the growing role of voice technology in healthcare to see where the industry is heading.
How Does It Handle Different Accents and Dialects?
This is a perfectly valid concern, and a testament to how far the technology has come. The leading voice AI systems are not just trained on a "standard" voice; they learn from vast, diverse datasets featuring speakers from all over the world.
The AI is smart enough to focus on phonetic patterns rather than memorizing a specific accent. This makes the software incredibly adaptable, whether your clinicians have a thick Southern drawl, a clipped British accent, or learned English as a second language.
Ready to cut your documentation time in half and get back to focusing on your patients? Whisperit provides a secure, AI-powered dictation platform built for the real-world demands of healthcare. Start your free trial today and experience the future of clinical documentation.