Security Control Framework: Your Complete Guide to Success
Understanding Why Security Control Frameworks Actually Matter
Implementing a robust security posture is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for organizations of all sizes. Instead of relying on a patchwork of ad-hoc security measures, a security control framework provides the structured approach needed to manage and mitigate cyber risks effectively. This framework serves as a blueprint for your organization's security, guiding everything from risk assessment to incident response. It helps transition from reactive firefighting to proactive defense.
The Importance of a Unified Security Approach
A core benefit of adopting a security control framework is the alignment it creates across an organization. It fosters a common language and shared understanding of security priorities. This ensures everyone, from IT staff to executives, is on the same page. This unified approach is particularly important in larger organizations where different teams may have competing priorities. A framework helps balance the needs of the development team to release software quickly with the security team's focus on secure software.
Transforming Theory into Practice
Security control frameworks are not meant to be static documents. They must be living tools that adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape. Successful security teams use these frameworks as roadmaps, constantly revisiting and refining them based on new threats, vulnerabilities, and business needs. This continuous improvement approach ensures the framework remains relevant and effective.

It's also important to acknowledge the growing prominence of certain frameworks within the industry. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) has become a widely recognized standard. In fact, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework boasts 68% adoption or valuation among cybersecurity professionals and organizations, making it the leading standard for guiding security controls, risk management, and incident response. This prevalence highlights the importance of staying informed about industry trends and adopting frameworks aligned with best practices. Find more detailed statistics here: NIST Ranked 2025's Most Valuable Cybersecurity Framework
Addressing Misconceptions and Ensuring Success
There are common misconceptions about security control frameworks. Some view them as overly complex or burdensome, hindering agility and innovation. However, when implemented correctly, a well-chosen framework can actually streamline security processes and improve efficiency. Check out our guide on Vendor Risk Assessment Templates. Another misconception is the idea of a one-size-fits-all solution. Choosing the right framework depends on various factors, including industry regulations, organizational maturity, and available resources.
Choosing the Right Security Control Framework
Selecting the appropriate framework requires a careful evaluation of your organization's specific needs and goals. This means considering factors such as the size and complexity of your IT infrastructure, the types of data you handle, and the regulatory requirements you must meet. You might be interested in: How to Master Vendor Risk Management. A thorough assessment will help you choose a framework that aligns with your business objectives and offers the most effective protection against relevant threats. This proactive approach to framework selection is crucial for ensuring your organization's long-term security posture.
Building Security Controls That Actually Protect Your Business

A security control framework provides the structure for a robust security posture. But having a framework alone isn't enough. This section explores the vital components needed to build controls that genuinely protect your business. Think of it like building a house: the blueprint (framework) is essential, but the materials and methods (controls) determine its strength.
The Three Pillars of Effective Control Systems
Effective security relies on three core pillars: administrative, technical, and physical controls. These elements work together to create a layered defense system. Administrative controls set the rules and procedures, shaping a security-conscious culture. Technical controls automate protection, acting as the digital locks and barriers. Physical controls protect tangible assets and limit facility access.
For example, requiring strong passwords (administrative), using multi-factor authentication (technical), and restricting server room access (physical) combine to form a strong defense against unauthorized access.
Administrative Controls: Shaping Security Culture
Administrative controls define how your organization handles security. These include the policies, procedures, and training that instill a security-first mindset. They encompass everything from background checks for new hires to mandatory security awareness training. These controls lay the foundation for a strong security culture.
Clear policies, regular training, and consistent enforcement demonstrate the importance of security to every employee. Documented incident response plans are also administrative controls, preparing for and coordinating the response to breaches. For more in-depth information, explore how to master data security best practices.
Technical Controls: Automated Protection
Technical controls are the digital safeguards that automate security and enforce policies. Examples include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. These tools constantly monitor and protect, serving as the first line of defense against cyber threats.
However, technical controls alone are insufficient. They must be correctly configured and integrated within the security framework. This often involves regular updates and maintenance to combat emerging threats.
Physical Controls: Protecting Tangible Assets
Physical controls safeguard physical access to your organization's assets. These include measures like security cameras, locked doors, and access badges. These fundamental controls prevent unauthorized physical access to sensitive data and equipment.
This is particularly vital in sectors handling sensitive data, like healthcare or finance. For example, physical access controls restrict data center entry, ensuring only authorized personnel can interact with critical infrastructure. Combining physical controls with administrative and technical safeguards provides comprehensive protection.
Balancing Security and Usability
While robust security is vital, it shouldn't hinder productivity. The objective is to find the balance between security and usability. Overly complex controls can frustrate employees, leading to workarounds that undermine security.
This means considering user experience when implementing security measures. Single sign-on solutions, for example, can enhance security while streamlining user access to multiple systems. This approach strengthens security without inconveniencing employees, promoting both security and productivity. User-friendly solutions empower employees to actively contribute to a strong security posture.
Mastering Risk-Based Security Approaches That Drive Results

Moving beyond basic compliance, a truly effective security control framework depends on understanding and mitigating the real risks to your business. This means shifting from a one-size-fits-all approach to a risk-based strategy. This strategy prioritizes vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. This section explores how to build a security posture that’s not just compliant, but truly resilient.
Assessing Your Assets and Identifying Vulnerabilities
The foundation of any risk-based approach is a comprehensive understanding of your assets. This goes beyond simply listing hardware and software. It involves identifying the critical data and processes essential to your operations. Once you know what truly matters, you can pinpoint the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat. For more information, see this article on how to conduct a risk assessment.
For example, a customer database is a crucial asset for most businesses. Potential vulnerabilities might include weak access controls, outdated software, or inadequate data backups. Identifying these vulnerabilities is the first step toward effectively mitigating them.
Threat Modeling: Understanding Real-World Attack Patterns
Understanding your vulnerabilities is essential. But knowing how attackers might exploit them is even more critical. This is where threat modeling comes in. Threat modeling involves analyzing potential attack scenarios and their likelihood. This helps you anticipate and defend against realistic threats.
This means going beyond hypothetical threats. Instead, focus on real-world attack patterns relevant to your industry and specific infrastructure. This targeted focus allows you to prioritize resources toward the most probable and impactful threats.
Quantifying Risk in Business Terms
While technical details are important, communicating risk to leadership requires speaking their language: business impact. This involves quantifying potential losses. Consider the financial impact, reputational damage, and operational disruption. Presenting this information allows leadership to make informed decisions about security investments.
This isn't about scaremongering. It's about presenting a clear, data-driven picture of the potential consequences of inadequate security. This data-driven approach ensures security priorities align with business objectives.
Maintaining a Dynamic Risk Monitoring System
The threat landscape is constantly evolving. This requires a dynamic risk monitoring system. The system must adapt to new vulnerabilities and attack vectors. Regular risk assessments, vulnerability scanning, and threat intelligence feeds are essential for maintaining an up-to-date understanding of your risk profile.
This proactive approach allows you to adjust your security controls and resource allocation as needed. It ensures your defenses remain effective against emerging threats. This continuous monitoring is crucial for a robust security posture.
Balancing Comprehensive Assessment with Resource Constraints
Ideally, organizations would conduct exhaustive risk assessments covering every possible scenario. However, resource constraints are a reality. This necessitates prioritizing assessments. Focus on the criticality of assets and the likelihood of specific threats.
This strategic approach maximizes the impact of your security investments. Concentrate on the areas that matter most. It acknowledges that perfect security is unattainable. But a risk-based approach helps achieve the best possible protection within your resource limitations.
Choosing The Framework That Fits Your Organization
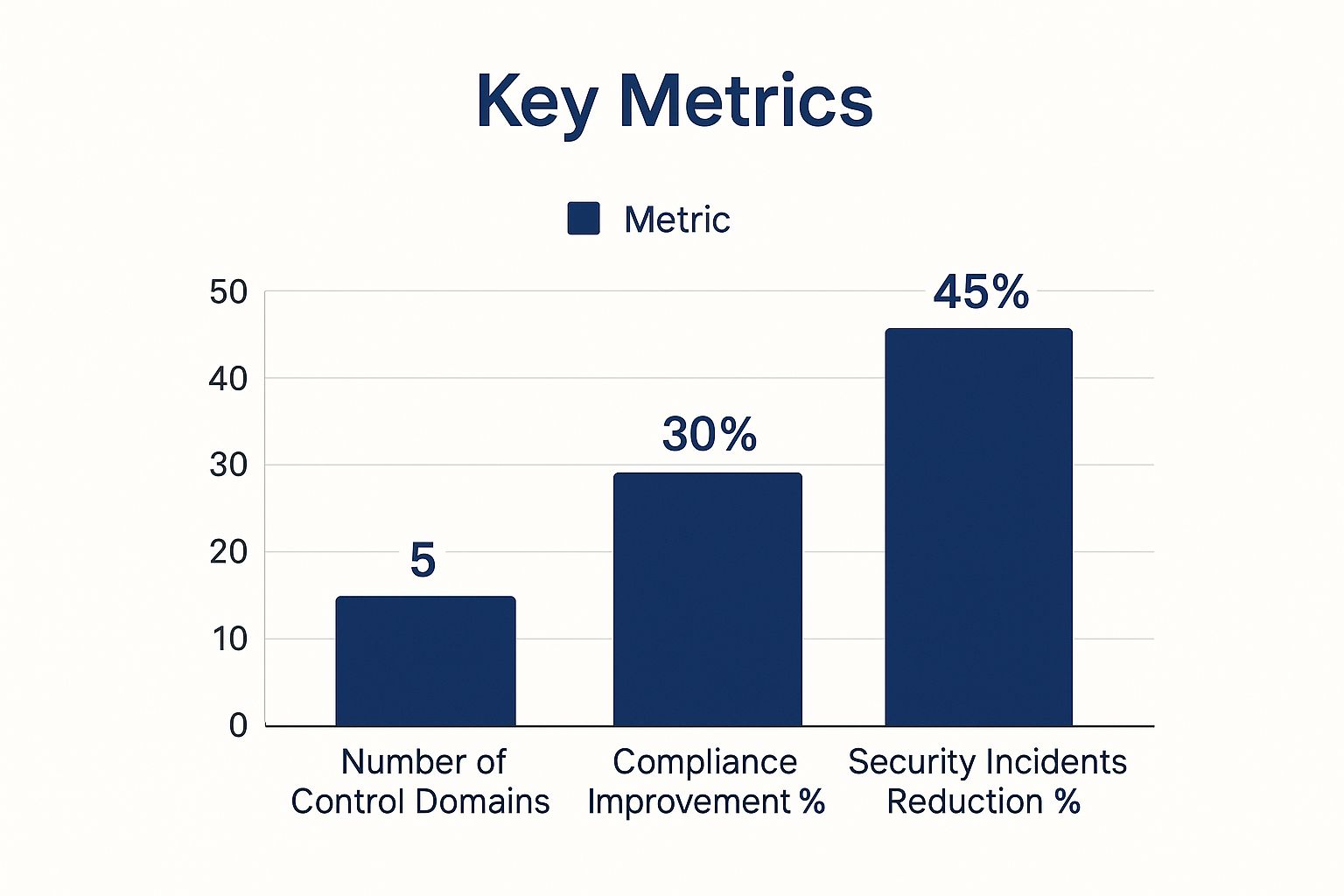
The infographic above illustrates the positive impact of a strong security control framework. It highlights improvements across key metrics, including the number of control domains, compliance, and security incidents. A well-implemented framework can significantly boost your security. You could see a 30% improvement in compliance and a 45% reduction in security incidents across 5 key control domains. This shows the importance of structured security management. Choosing the right framework is key. For more information, check out this helpful blog post: Choosing Your Compliance Framework.
Evaluating Your Options: NIST, ISO 27001, CIS Controls, and More
The sheer number of security control frameworks can be daunting. From NIST and ISO 27001 to the CIS Controls, many options exist. Each framework has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Making the right choice for your organization means carefully considering your unique needs. Don't just follow industry trends or accept generic advice.
Key Criteria for Framework Selection
Several factors should guide your decision-making process. Consider your organization's maturity level. Are you starting from the beginning or enhancing current security measures? Some frameworks, like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, offer flexibility for organizations at different stages.
Next, assess your resources. Frameworks like ISO 27001 demand considerable time, budget, and expertise.
Finally, consider your regulatory requirements. Industries like healthcare and finance face specific compliance rules. These might require frameworks like HIPAA or SOC 2.
To help visualize the differences between these frameworks, let's look at a comparison matrix.
The table below, "Security Framework Comparison Matrix," offers a comprehensive comparison of major security frameworks, highlighting their adoption rates, complexity levels, and best use cases. This information can help you quickly identify which framework might be most appropriate for your specific needs.
| Framework | Adoption Rate | Implementation Complexity | Best For | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | High | Moderate | Organizations of all sizes and maturity levels | Flexible, risk-based approach |
| ISO 27001 | Moderate | High | Organizations with mature security practices seeking international recognition | Comprehensive, globally recognized standard |
| CIS Controls | Moderate | Moderate | Organizations looking for practical, actionable guidance | Prescriptive, focused on technical controls |
| HIPAA | High (in healthcare) | High | Healthcare organizations | Protects patient health information |
| SOC 2 | Moderate (in specific industries) | High | Service providers demonstrating security controls to clients | Focuses on trust and data protection |
As you can see, each framework caters to different needs and situations. NIST is a flexible option for various maturity levels. ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive standard, but it’s more complex. CIS Controls offer practical guidance with a focus on technical controls. HIPAA and SOC 2 are industry-specific and address distinct compliance requirements.
Adapting Frameworks to Your Business Needs
While following core principles is important, security frameworks aren't set in stone. Effective security teams adapt frameworks to their specific business contexts. This might mean modifying specific controls or adding new ones. The goal is to ensure the framework remains effective and aligns with your operational needs. For further insight, consider reading this blog post: How to master security audits.
Recognizing When a Framework Isn't the Right Fit
Sometimes, a framework just doesn't work. Warning signs include overwhelming complexity, poor integration with current processes, and lack of team support. If these occur, reassess your needs and consider other options. Don’t be afraid to change your approach. Flexibility is essential in security.
Securing Applications Within Your Control Framework
Application security is no longer a peripheral concern. It's fundamental to any modern security program. This requires integrating security into every phase of the application lifecycle. A robust security control framework provides the necessary structure to implement these essential practices, ensuring a consistent approach to application security across your organization.
Integrating Application Security Into Your Framework
Organizations that prioritize security embed it throughout their control frameworks. This covers everything from the initial design and development phases to deployment and ongoing maintenance. This integration is vital. It prevents security from being an afterthought, tacked on at the end of the development process.
This integrated approach ensures security is addressed from the very beginning, influencing design choices, coding standards, and testing procedures. This proactive stance significantly reduces potential vulnerabilities and strengthens the overall security posture of your applications.
Practical Approaches for Securing Different Application Types
Different applications have unique security needs. Web applications, for example, commonly face threats like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection. Mobile apps grapple with vulnerabilities related to data storage and device access. APIs require strong authentication and authorization mechanisms. Cloud environments introduce unique concerns regarding access management and data protection.
Addressing these diverse threats requires specific security approaches. A security control framework provides a standardized method for assessing risks and implementing suitable safeguards for each type of application. This structured method ensures consistent security across your application portfolio.
Implementing Security Testing, Code Reviews, and Vulnerability Management
Effective application security relies on proactive measures. Security testing identifies vulnerabilities before deployment. Code reviews help ensure adherence to secure coding guidelines. Vulnerability management processes track and address identified weaknesses. Incorporating these processes into your security control framework ensures consistent and effective implementation. For instance, automated security testing tools can be integrated into the development pipeline, catching vulnerabilities early in the process.
This systematic approach is crucial as development speeds increase, ensuring security keeps pace with new features and functionalities. The application security market’s growth reflects its increasing importance. In 2024, the U.S. market was valued at nearly $19.89 billion, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 14.8% from 2020 to 2024. Discover more about the application security market's growth. Find more detailed statistics here.
Balancing Security and Development Velocity
Balancing security with the demand for rapid development is a common challenge. Overly strict security practices can slow development teams and stifle innovation. However, neglecting security can lead to expensive breaches and damage your reputation.
A well-designed security control framework helps strike this balance. By automating security processes and integrating them into development workflows, organizations can achieve strong security without compromising speed. This makes security a driver of innovation, not an obstacle.
Building Security Into DevOps Workflows
DevOps emphasizes collaboration and automation. Integrating security into DevOps, often called DevSecOps, ensures security is a core component of the development process from the outset. This approach promotes shared responsibility for security between development and operations teams.
Practical strategies include integrating security testing tools into the continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline and providing developers with security training. This collaborative approach fosters a security-conscious culture throughout the development lifecycle, promoting proactive security practices instead of reactive responses to vulnerabilities.
Proving Your Security Investment Actually Works
Moving beyond simple compliance checklists is crucial. It's about demonstrating the real value of your security investments to business leadership. This section explains how successful security teams measure the effectiveness of their security control framework using metrics that resonate with executives and stakeholders.
Establishing Security Baselines and Tracking Progress
Before measuring improvement, you need a starting point. Establishing a security baseline involves assessing your current security posture. This includes identifying existing vulnerabilities, documenting current security controls, and quantifying key metrics like incident rates and remediation times. This baseline serves as the benchmark against which future progress is measured.
Tracking progress requires continuous monitoring of these key metrics. This lets you see how your security control framework is impacting your overall security posture over time. This data-driven approach provides tangible evidence of your security investments' effectiveness.
Calculating ROI: Risk Reduction and Operational Benefits
Demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of a security control framework goes beyond simple cost savings. While reduced incident costs are a factor, the true ROI includes avoiding the potentially devastating financial and reputational damage from major breaches. A well-implemented framework can also streamline operations, improving efficiency and reducing administrative overhead.
For example, automating security tasks like vulnerability scanning and patch management not only strengthens security but also frees up IT staff for other strategic initiatives. This dual benefit showcases the framework's value to both security and business operations. You might be interested in: How to master data privacy compliance frameworks.
Translating Technical Improvements Into Business Impact
Technical security improvements often don't resonate with business leaders. Translating these improvements into business-relevant terms is essential. This involves demonstrating how stronger security directly supports business objectives.
For example, a reduced risk of data breaches translates into maintaining customer trust and avoiding regulatory fines. Improved system uptime means increased productivity and revenue generation. Presenting this information clearly and concisely ensures business leaders understand the security control framework's value proposition.
Dashboard and Reporting Strategies: Telling a Compelling Story
Effective dashboards and reports tell a story about your security program's value. They visually represent key metrics, trends, and progress toward security goals. This visual approach simplifies complex data, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp the framework's effectiveness.
Avoid vanity metrics that look impressive but lack substance. Focus on metrics that demonstrate tangible improvements, such as reduced incident rates, faster remediation times, and improved compliance with regulatory requirements. When securing applications within your control framework, consider reviewing recommended standards for Web Application Security Best Practices.
The global security market, encompassing both physical and cybersecurity controls, highlights the importance of frameworks. Valued at approximately $150.39 billion** in 2024, this market is projected to exceed **$311.08 billion by 2033, showing a CAGR of 8.34%. Learn more about security market growth here.
Key Metrics for Measuring Framework Effectiveness
The following table provides examples of key performance indicators and measurement criteria for evaluating security control framework effectiveness and return on investment.
| Metric Category | Key Indicators | Measurement Method | Target Range | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Reduction | Number of critical vulnerabilities | Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing | < 10 open critical vulnerabilities | Reduced likelihood of successful attacks |
| Incident Response | Mean time to detect (MTTD) | Security information and event management (SIEM) system | < 24 hours | Faster containment and reduced damage from incidents |
| Compliance | Percentage of compliance requirements met | Audits and compliance reports | > 95% | Avoids regulatory fines and penalties |
| Operational Efficiency | Automation of security tasks | Percentage of automated security processes | > 75% | Frees up IT staff for strategic initiatives |
By focusing on these key areas, you can effectively communicate your security control framework's value to business leadership and ensure continued support for your security program.