6 Incident Response Plan Example Templates for 2025
Navigating the Cybersecurity Landscape: Why You Need a Robust Incident Response Plan
Cybersecurity incidents pose a constant threat. A robust incident response plan is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring business continuity. This listicle provides six leading incident response plan examples based on established frameworks: NIST, SANS, ISO 27035, CISA, ENISA, and the Cloud Security Alliance. By understanding these frameworks, legal professionals, healthcare providers, and security/compliance officers can select and adapt the best approach for their organization, creating a comprehensive incident response plan example tailored to their specific needs.
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework Incident Response Plan
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) Incident Response Plan offers a robust and structured approach to managing cybersecurity incidents. Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this framework provides organizations with a set of best practices and guidelines to effectively identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents. It emphasizes a risk-based approach, allowing organizations to tailor their incident response capabilities to their specific needs and risk tolerance. This framework is not just a static document; it promotes continuous improvement and risk management throughout the incident lifecycle, ensuring organizations are constantly evolving their defenses.

The NIST CSF Incident Response Plan revolves around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. The Identify function focuses on understanding the organization's assets, systems, and data, as well as the associated risks. Protect emphasizes implementing safeguards to limit or contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity incident. Detect involves implementing measures to identify security events and incidents in a timely manner. Respond outlines the actions to be taken to contain and eradicate an incident once it's detected. Finally, Recover focuses on restoring affected systems and services back to normal operations.
This framework's strength lies in its flexibility and scalability. It can be adopted by organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises, and across various industries. The risk-based approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively, focusing on the most critical threats. The framework's emphasis on stakeholder communication ensures that all relevant parties, including legal, security, and executive leadership, are kept informed throughout the incident lifecycle. For legal professionals, this provides a clear structure for evidence collection and legal action. Healthcare providers benefit from its alignment with HIPAA compliance requirements. Security and compliance officers leverage the framework for developing and implementing robust incident response programs.
Several prominent organizations have successfully implemented the NIST CSF Incident Response Plan. Major financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase utilize it to safeguard sensitive financial data and maintain operational resilience. Healthcare systems have adopted the framework to achieve HIPAA compliance and protect patient information. Government agencies and contractors leverage the NIST CSF to enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect critical infrastructure. Learn more about NIST Cybersecurity Framework Incident Response Plan These examples demonstrate the framework's versatility and effectiveness in diverse environments.
While the NIST CSF Incident Response Plan offers numerous benefits, it's important to acknowledge some potential challenges. For smaller organizations with limited resources, the framework's comprehensive nature can be complex and require significant investment. Customization might be necessary for specific industries to address unique regulatory requirements. The initial implementation can be time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution.
To ensure successful implementation of the NIST CSF Incident Response Plan, consider the following tips:
- Start with a risk assessment: Prioritize implementation efforts by identifying the most critical assets and vulnerabilities.
- Begin with the core functions: Focus on implementing the five core functions (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover) before adding further complexity.
- Ensure executive leadership buy-in: Secure support from senior management early in the process to allocate necessary resources and facilitate implementation.
- Integrate with existing security tools and processes: Leverage current security investments to streamline implementation and avoid redundancy.
- Regular training and tabletop exercises: Conduct regular training sessions and tabletop exercises to test and refine the incident response plan, ensuring preparedness for real-world incidents.
The NIST CSF Incident Response Plan is a valuable resource for any organization seeking to improve its cybersecurity posture. Its comprehensive approach, scalability, and focus on risk management make it an excellent choice for organizations looking to meet regulatory requirements and effectively manage cybersecurity incidents. While implementation can be challenging, the long-term benefits of a robust incident response plan far outweigh the initial investment. The framework’s widespread adoption, popularized by NIST, the Department of Homeland Security, and major cybersecurity consulting firms, underscores its importance as a leading standard for incident response.
2. SANS Incident Response Methodology
The SANS Institute's six-step incident response methodology provides a structured, practical approach for handling security incidents, making it a crucial element of any robust incident response plan example. This methodology emphasizes preparation, swift identification, effective containment, complete eradication of threats, efficient recovery, and valuable lessons learned. Its strong focus on digital forensics and evidence preservation makes it especially relevant for legal professionals, healthcare providers, and security and compliance officers dealing with sensitive data and potential legal ramifications. This approach deserves its place on this list due to its comprehensive nature, proven effectiveness, and widespread adoption by industry leaders.
The SANS methodology works by guiding organizations through a systematic process to address security incidents efficiently and effectively. It starts with thorough preparation, enabling organizations to be proactive rather than reactive. Once an incident is identified, the methodology outlines steps for containment to limit the damage. Eradication removes the threat entirely, while recovery focuses on restoring systems and operations. Finally, the lessons learned phase ensures continuous improvement by analyzing the incident and updating the response plan.
One of the core strengths of the SANS methodology is its focus on digital forensics. This allows organizations to gather and preserve crucial evidence for potential legal proceedings or regulatory investigations. The detailed documentation requirements further support this by providing a comprehensive record of the incident and the actions taken. The integration of threat intelligence ensures that the response is tailored to the specific threat landscape, while the incident classification and prioritization system allows resources to be allocated effectively.
The SANS methodology boasts several advantages:
- Practical and actionable guidance: The clear, step-by-step procedures provide a roadmap for even complex incident response scenarios.
- Strong forensic focus: Emphasis on evidence preservation and chain of custody is invaluable for legal and regulatory compliance.
- Excellent training materials: SANS offers extensive resources and training to equip incident response teams with the necessary skills.
- Battle-tested by security professionals: The methodology is widely used and trusted by security experts worldwide.
However, like any methodology, the SANS approach has some potential drawbacks:
- Resource-intensive: Implementing the full methodology can be challenging for smaller teams with limited resources.
- Technical focus: The emphasis on technical aspects may sometimes overshadow the business impact of an incident.
- Requires specialized skills: Effective implementation requires specialized forensic and security expertise.
- Documentation overhead: The extensive documentation requirements can sometimes slow down the initial response.
The SANS methodology has been successfully implemented by numerous organizations, including Fortune 500 companies' Security Operations Centers (SOCs), law enforcement cybercrime units, and managed security service providers. It has also been utilized in several high-profile breach investigations, demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
To effectively implement the SANS Incident Response Methodology, consider these tips:
- Invest in preparation: A well-defined plan, trained personnel, and readily available tools are essential for a successful response.
- Develop standardized toolkits: Having pre-configured tools and resources can save valuable time during an incident.
- Create detailed playbooks: Develop specific playbooks for common incident types to streamline response efforts.
- Establish clear communication channels: Effective communication is critical throughout the incident response process.
- Regular hands-on training: Conduct regular training exercises with real-world scenarios to prepare your team.
The following infographic illustrates the initial steps of the SANS Incident Response process: Preparation, Identification, and Containment. This visualization showcases the crucial flow of actions required in the early stages of an incident.
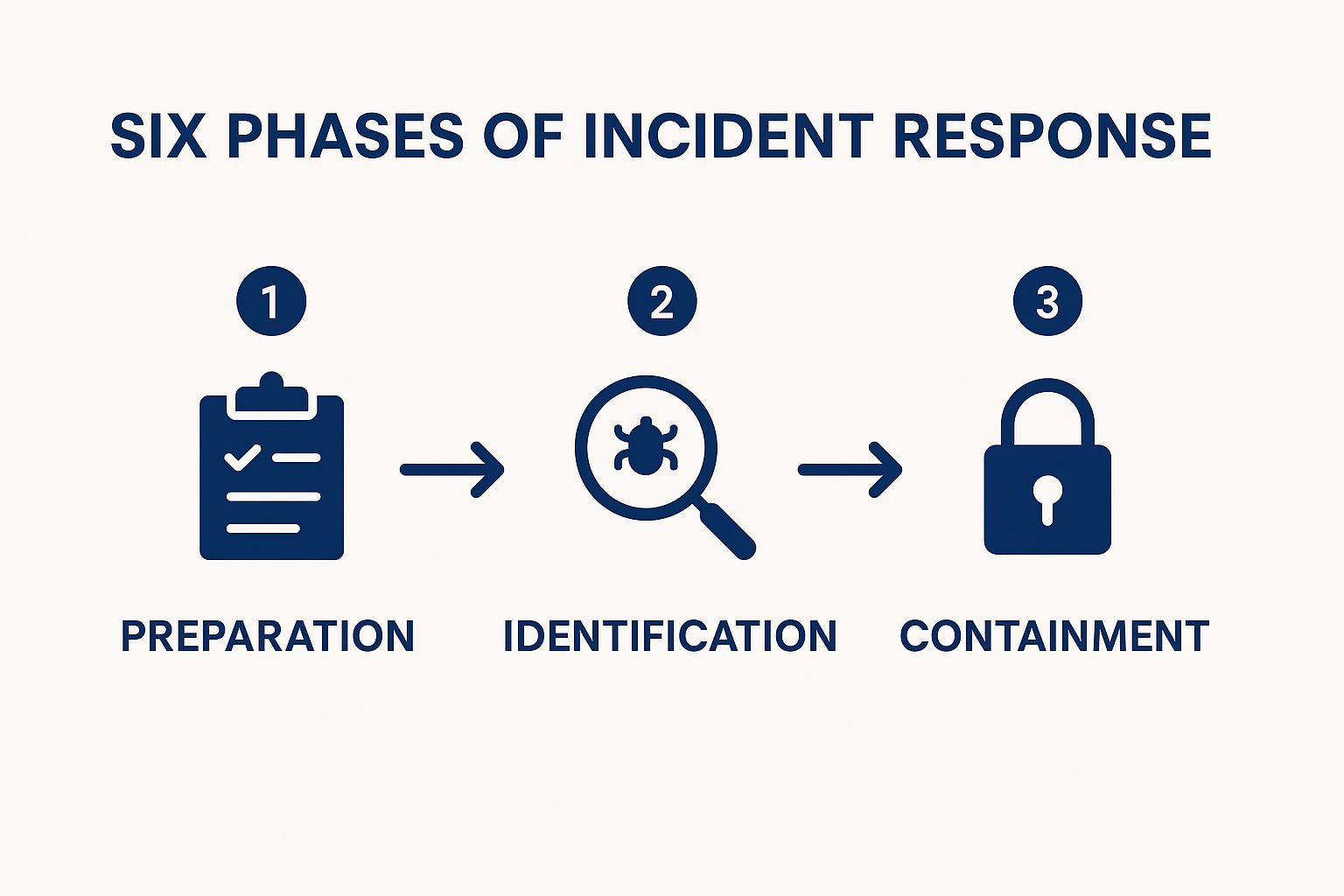
The infographic demonstrates the logical progression of the SANS methodology, highlighting the importance of preparation before an incident occurs and the swift actions required for identification and containment to limit the impact. The interconnectedness of these phases emphasizes that a strong foundation in preparation is crucial for effective identification and containment.
Learn more about SANS Incident Response Methodology This link may provide additional context on risk assessments, which is a vital component of the preparation phase of the SANS methodology. When and why to use this approach depends heavily on the needs of the organization, but its structured approach and focus on forensics make it a compelling choice for those handling sensitive data. Understanding the potential legal and compliance implications of a data breach makes the SANS methodology a highly relevant incident response plan example.
3. ISO 27035 Incident Management Standard
When crafting a robust incident response plan, looking to established frameworks can provide valuable structure and guidance. The ISO 27035 Incident Management Standard offers a comprehensive, internationally recognized approach to handling information security incidents. It provides a structured, five-phase process for managing incidents, from detection and reporting through to recovery and post-incident review. This standard emphasizes organizational readiness, risk-based assessment, and continuous improvement, making it a powerful tool for organizations seeking a mature and effective incident response plan example.

ISO 27035 promotes a proactive approach to incident management, focusing on establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and procedures before an incident occurs. This proactive stance is crucial for minimizing the impact of security breaches and ensuring a swift, coordinated response. The five-phase process outlined in the standard covers: Planning, Detection & Reporting, Assessment & Decision Making, Response & Recovery, and Post Incident Review. This cyclical process ensures continuous learning and improvement of the incident response capabilities. The standard also stresses the importance of integrating incident management with the broader information security management system (ISMS), particularly aligning with ISO 27001 requirements.
One of the key strengths of ISO 27035 is its risk-based approach to incident assessment and prioritization. This allows organizations to allocate resources effectively, focusing on the incidents that pose the greatest threat to their business. The standard also provides frameworks for stakeholder communication, ensuring that all relevant parties are kept informed throughout the incident lifecycle. This is particularly important for legal professionals, healthcare providers, and security and compliance officers who need to navigate regulatory requirements and maintain public trust. Furthermore, the emphasis on metrics and continuous improvement helps organizations track their performance and identify areas for enhancement.
Several organizations have successfully implemented ISO 27035, demonstrating its practical value. Multinational corporations have adopted it to ensure global consistency in their incident response processes. Organizations pursuing ISO 27001 certification often integrate ISO 27035 to fulfill the incident management requirements. European companies leverage it to support their GDPR compliance efforts, and government agencies worldwide utilize it to strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
While ISO 27035 offers numerous advantages, it's important to be aware of the potential drawbacks. Its comprehensive nature can lead to bureaucratic processes and extensive documentation. Implementing the standard can be complex and time-consuming, requiring strong management support and commitment. While it excels in management and governance, it may not provide the same level of technical detail as some other frameworks.
To effectively implement ISO 27035, consider the following tips:
- Align implementation with existing ISO management systems: Leverage existing frameworks to streamline the integration process.
- Focus on policy development before technical implementation: Establish clear policies and procedures to guide the incident response process.
- Ensure strong management support and governance: Secure buy-in from senior management to ensure adequate resources and commitment.
- Integrate with business continuity planning: Align incident response with business continuity plans to minimize disruption during an incident.
- Regular management reviews and updates: Conduct periodic reviews to assess the effectiveness of the incident response plan and make necessary adjustments.
If you’re considering ISO 27001 certification, learning more about the related ISO 27035 can be incredibly beneficial. Learn more about ISO 27035 Incident Management Standard
By understanding the intricacies of the ISO 27035 Incident Management Standard and implementing it effectively, organizations can build a robust and resilient incident response capability, minimizing the impact of security incidents and protecting their valuable assets. This framework offers a solid foundation for any incident response plan example, providing a structured approach to navigating complex security events.
4. CISA Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Template
When crafting an incident response plan example, especially for organizations operating within the highly regulated landscapes of government, critical infrastructure, or those handling sensitive data like legal and healthcare professionals, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Template stands out as a robust and comprehensive resource. This government-developed template offers detailed guidance on planning, execution, and recovery from cybersecurity incidents, emphasizing coordination with government agencies and adherence to stringent information sharing requirements. This section will delve into the template's features, benefits, drawbacks, and its suitability for various organizations seeking a structured approach to incident response.
The CISA template isn't just a generic framework; it's meticulously designed to address the specific needs of federal agencies and critical infrastructure organizations. It incorporates government-specific reporting requirements, integrates with national cybersecurity frameworks, and places a strong emphasis on protecting vital assets. This focus stems from the understanding that these entities are prime targets for cyberattacks and play a critical role in national security and public well-being. For instance, a healthcare provider handling protected health information (PHI) or a legal professional dealing with confidential client data needs a robust incident response plan that aligns with HIPAA and other relevant regulations. The CISA template offers a solid foundation for building such a plan.
One of the template's core strengths lies in its detailed coordination procedures with CISA and its emphasis on threat intelligence sharing. This allows organizations to leverage the expertise and resources of a leading cybersecurity authority, facilitating faster and more effective responses to incidents. Imagine a scenario where a government contractor detects a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting its employees. By utilizing the CISA template, the contractor can quickly report the incident to CISA, share gathered threat intelligence, and receive guidance on containment and mitigation strategies, minimizing the potential damage.
Another key advantage of the CISA template is its compliance with federal mandates and regulations. This is particularly crucial for government agencies and contractors who must adhere to strict cybersecurity standards. Implementing the template ensures that these organizations are prepared to meet these requirements and demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity best practices. Similarly, healthcare providers can leverage the template to align their incident response plans with HIPAA requirements for breach notification and data recovery. Learn more about CISA Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Template
While the CISA template offers numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge its potential drawbacks. Its complexity and heavy compliance and reporting burden might be overwhelming for smaller private sector organizations with limited resources. The template’s focus on government coordination may not be directly applicable to all industries, and the limited customization options might require significant adaptation for specific organizational needs. For instance, a small law firm might find the extensive reporting requirements cumbersome, while a large multinational corporation might need to tailor the template to its specific industry regulations and internal policies.
Despite these limitations, the CISA template provides an invaluable resource for developing a comprehensive incident response plan, particularly for organizations operating in high-stakes environments. Its rigorous structure, emphasis on information sharing, and alignment with federal regulations offer a strong foundation for incident preparedness and response. Examples of successful implementation can be seen across various levels of government and within critical infrastructure sectors. Federal agencies and departments, state and local governments, critical infrastructure operators, and government contractors have all adopted and adapted the CISA template to bolster their cybersecurity posture.
For those considering adopting the CISA template, here are some actionable tips:
- Understand federal reporting requirements thoroughly. Familiarize yourself with the specific reporting obligations outlined in the template and ensure your organization has the necessary processes in place to comply.
- Establish relationships with CISA before incidents occur. Building proactive communication channels with CISA will facilitate smoother collaboration during a crisis.
- Customize the template for organizational needs. While the template provides a strong foundation, tailor it to reflect your organization's specific industry, size, and risk profile.
- Regular coordination exercises with government partners. Conducting drills and simulations based on the template will help refine your incident response capabilities and strengthen collaboration with government agencies.
- Stay updated on changing federal requirements. Cybersecurity regulations and best practices are constantly evolving. Regularly review and update your incident response plan to maintain compliance and effectiveness.
The CISA Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Template deserves its place in any discussion of incident response plan examples due to its rigorous approach, government backing, and focus on critical infrastructure protection. While it might not be a one-size-fits-all solution, it provides a valuable framework for organizations seeking to build a robust and compliant incident response capability, particularly those within the public sector, critical infrastructure, and industries handling sensitive information. Understanding its features, benefits, and limitations allows organizations to leverage its strengths and adapt it to their unique needs, ultimately enhancing their ability to effectively respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents.
5. ENISA Good Practice Guide for Incident Management
When crafting a robust incident response plan, especially within the European Union or for organizations operating within its borders, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity's (ENISA) Good Practice Guide for Incident Management provides an invaluable framework. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for establishing, operating, and maturing Computer Security Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs), emphasizing European regulatory compliance and cross-border incident coordination. This makes it a critical incident response plan example for organizations navigating the complex EU cybersecurity landscape.
ENISA's guide offers detailed operational guidance, covering all aspects of CSIRT lifecycle management. This includes establishing a CSIRT from the ground up, defining its scope and responsibilities, outlining incident handling procedures, and ensuring effective communication and collaboration within the organization and with external stakeholders. It also stresses the importance of threat intelligence sharing and regular training and awareness programs to proactively enhance incident response capabilities.
A key differentiator of this framework is its alignment with European regulations. It provides specific guidance on complying with legislation like the Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive, a foundational piece of EU cybersecurity legislation, and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which has significant implications for data breach notifications and incident response. This focus on compliance makes the guide especially relevant for legal professionals, healthcare providers, and security and compliance officers operating within the EU.
Features and Benefits:
- CSIRT Establishment and Operational Guidance: Provides step-by-step guidance on setting up and running a CSIRT, covering areas like incident identification, analysis, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity.
- European Regulatory Compliance Focus: Aligns incident response procedures with the NIS Directive, GDPR, and other relevant EU regulations, minimizing legal and financial risks.
- Cross-border Incident Coordination Procedures: Outlines best practices for collaborating with other CSIRTs and authorities across borders, crucial for incidents with international implications.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Communication Strategies: Emphasizes effective communication with internal and external stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and law enforcement.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing Frameworks: Promotes the sharing of threat information within and across organizations to enhance collective cybersecurity resilience.
- Training and Awareness Program Guidance: Provides recommendations for developing training programs to improve incident response skills and security awareness across the organization.
Pros:
- Tailored for the European Regulatory Environment: Offers a clear path to compliance with complex EU regulations, minimizing legal risks and potential penalties.
- Strong Focus on International Cooperation: Facilitates cross-border incident collaboration, which is essential in today's interconnected world.
- Comprehensive CSIRT Operational Guidance: Covers all aspects of CSIRT management, providing a robust foundation for incident response capabilities.
- Regular Updates based on EU Threat Landscape: ENISA regularly updates the guide to reflect the evolving threat landscape and regulatory environment.
- Excellent for GDPR Compliance: Provides specific guidance on meeting GDPR requirements for data breach notifications and incident response.
Cons:
- Primarily Focused on European Context: While offering valuable best practices, its primary focus on EU regulations might not directly translate to other jurisdictions.
- May Not Align with Non-EU Regulations: Organizations operating outside the EU might need to adapt the framework to align with local laws and regulations.
- Complex Multi-jurisdictional Requirements: Implementing the guide can be challenging for organizations operating across multiple EU member states, requiring careful consideration of varying national implementations of EU directives.
- Heavy Emphasis on Regulatory Compliance: While crucial, the strong focus on compliance can sometimes overshadow other critical aspects of incident response, such as technical remediation and business continuity.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- European telecommunications companies have adopted ENISA's framework to strengthen their incident response capabilities and ensure compliance with the NIS Directive.
- EU member state national CSIRTs utilize the guide to standardize their operations and facilitate cross-border collaboration.
- European financial institutions leverage the framework to enhance their resilience against cyberattacks and comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
- Multinational corporations operating in the EU adopt ENISA's guidelines to navigate the complex European cybersecurity landscape.
Tips for Implementation:
- Understand NIS Directive Requirements Thoroughly: Familiarize yourself with the NIS Directive and its specific requirements for incident reporting and information sharing.
- Establish Relationships with National CSIRTs: Build strong relationships with relevant national CSIRTs to facilitate communication and collaboration in case of cross-border incidents.
- Focus on Cross-border Communication Procedures: Develop clear procedures for communicating and collaborating with other CSIRTs and authorities in different EU member states.
- Regular Participation in European Cybersecurity Exercises: Participate in cybersecurity exercises organized by ENISA and other European bodies to test and improve your incident response capabilities.
- Stay Updated on EU Cybersecurity Regulations: Continuously monitor changes and updates to EU cybersecurity regulations and adapt your incident response plan accordingly.
By utilizing the ENISA Good Practice Guide for Incident Management as an incident response plan example, organizations can build a robust and compliant framework to effectively manage security incidents and protect their operations within the complex European digital landscape. You can find the latest version of the guide on the ENISA website.
6. Cloud Security Alliance Incident Response Framework
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Incident Response Framework provides a structured approach to handling security incidents specifically within cloud environments. Unlike traditional incident response plans, this framework acknowledges the unique characteristics of the cloud, such as multi-tenancy, data distribution across geographical locations, jurisdictional variations in legal requirements, and the shared responsibility model between cloud providers and their customers. This focus makes it an invaluable tool for any organization operating in the cloud. This framework offers practical guidance for both cloud service providers, responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, and cloud customers, responsible for securing their own data and applications within that infrastructure.

The CSA framework works by outlining a series of stages for incident response, including preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity. Within each stage, the framework provides cloud-specific considerations and recommendations. For instance, during the identification phase, it emphasizes the importance of leveraging cloud-native security monitoring tools to detect anomalous activity. In the containment phase, it addresses the complexities of isolating affected systems in a multi-tenant environment. This detailed, stage-by-stage guidance ensures a comprehensive and effective response to security incidents in the cloud.
One of the key strengths of the CSA framework is its emphasis on the shared responsibility model. It clarifies the roles and responsibilities of both the cloud provider and the customer in various incident scenarios, which is crucial for a coordinated and efficient response. For example, if a data breach occurs due to a vulnerability in the underlying infrastructure, the cloud provider is primarily responsible for addressing the vulnerability. However, the customer is responsible for mitigating the impact on their own data and applications. This clear delineation of responsibilities helps prevent confusion and delays during an incident.
Examples of successful implementation of the CSA framework are widespread. Major cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft, and Google have integrated its principles into their own incident response procedures. Enterprises with hybrid cloud architectures leverage the framework to bridge the gap between their on-premises and cloud security practices. Cloud-native startups and companies, often heavily reliant on cloud services, rely on the CSA framework to build robust security postures from the ground up. Even managed cloud service providers use the framework to ensure the security of their clients' cloud environments.
When and why should you use this approach? If your organization utilizes cloud services in any capacity, the CSA framework is highly relevant. Whether you are a healthcare provider storing patient data in the cloud, a legal professional managing sensitive client information online, or a security and compliance officer responsible for overall organizational security, this framework can equip you with the necessary tools and knowledge to effectively respond to cloud-related security incidents.
Here are some actionable tips for implementing the CSA Framework:
- Understand shared responsibility models clearly: Work with your cloud provider to clearly define responsibilities in various incident scenarios.
- Establish incident response procedures with cloud providers: Coordinate your incident response plan with your provider's procedures to ensure seamless collaboration.
- Implement cloud-native security monitoring tools: Utilize tools designed specifically for cloud environments to effectively detect and respond to threats.
- Regular testing in cloud environments: Conduct regular incident response drills in your cloud environment to identify gaps and improve your response capabilities.
- Stay updated on cloud provider security capabilities: Keep abreast of your cloud provider's security updates and features to leverage the latest security advancements.
Pros and Cons of the CSA Framework:
Pros:
- Specifically designed for cloud environments
- Addresses unique cloud security challenges
- Covers both provider and customer perspectives
- Strong focus on emerging cloud technologies
- Regular updates for evolving cloud landscape
Cons:
- Limited to cloud-specific scenarios, may not fully address on-premise incidents.
- Can be complex to implement in multi-vendor cloud environments.
- The rapidly changing cloud technology landscape requires continuous adaptation.
The CSA Incident Response Framework deserves a prominent place in any incident response plan example because it addresses the unique challenges of the cloud era. By providing a structured approach, clarifying responsibilities, and offering practical guidance, it empowers organizations to effectively manage security incidents in the cloud. Learn more about Cloud Security Alliance Incident Response Framework and enhance your cloud security posture.
6 Incident Response Plans Compared
| Framework / Plan | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework Incident Response Plan | High - comprehensive and customizable | High - requires significant investment | Robust incident lifecycle management | Regulated industries, large orgs, compliance focus | Widely recognized, risk management, regulatory compliance |
| SANS Incident Response Methodology | Moderate to High - detailed, step-wise process | Moderate to High - forensic skills needed | Effective forensic evidence handling | Forensic-heavy investigations, SOC teams | Practical, strong forensic focus, well-documented |
| ISO 27035 Incident Management Standard | High - process-heavy and bureaucratic | Moderate to High - documentation intense | Strong organizational governance | Multinationals, ISO 27001 certified orgs | Internationally accepted, integrates with ISO suite |
| CISA Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Template | Moderate - government-specific but template-based | Moderate - coordination and compliance | Coordinated federal-level incident response | Federal agencies, critical infrastructure | Government tailored, free, strong focus on info sharing |
| ENISA Good Practice Guide for Incident Management | Moderate to High - regulatory and cross-border complexity | Moderate - emphasis on communication | Enhanced EU regulatory compliance | European orgs, cross-border incident coordination | EU focused, international cooperation, GDPR compliance |
| Cloud Security Alliance Incident Response Framework | Moderate - cloud-specific environment focus | Moderate - cloud tools and expertise | Cloud-adapted incident detection & response | Cloud providers, hybrid environments | Addresses unique cloud challenges, provider & customer focus |
Building Your Cybersecurity Fortress: Choosing the Right Incident Response Framework
Effectively responding to cybersecurity incidents requires a well-defined plan based on a robust framework. This article explored several leading incident response plan examples, including the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, SANS Incident Response Methodology, ISO 27035, CISA's template, ENISA's guide, and the Cloud Security Alliance framework. Each offers a structured approach to incident management, from preparation and identification to containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity. The key takeaway is that no single framework is universally perfect; the best choice depends on your organization's specific needs, industry regulations, and risk tolerance. Mastering these concepts and choosing the right incident response plan example for your organization is crucial for minimizing downtime, mitigating financial losses, preserving your reputation, and maintaining the trust of your clients and partners.
When choosing an incident response framework, consider incorporating automation tools to streamline workflows. For example, solutions like automated ticket routing can significantly improve response times and resource allocation during a security event. By implementing a comprehensive incident response plan and leveraging best practices, you are proactively building a strong cybersecurity fortress to protect your valuable data and ensure business continuity in today's increasingly complex threat landscape.
Streamline your incident response communication and documentation with Whisperit, an AI-powered dictation and documentation tool designed to seamlessly integrate with any incident response framework. Whisperit empowers your team to manage incidents efficiently and effectively, from initial reporting through post-incident analysis. Explore Whisperit today and fortify your incident response strategy.