How to Transcribe an Audio File A Practical Guide
When you need to transcribe an audio file, you've got two main paths to choose from: a quick, automated transcription using an AI service or a more hands-on manual transcription for top-notch accuracy. The best route really hinges on the quality of your audio, how quickly you need it back, and your budget.
Choosing Your Transcription Game Plan
Before you hit "transcribe," take a moment to think about your end goal. This isn't just a tech choice; it's about matching the method to what you actually need. Are you turning a fast-paced podcast into a blog post where getting the bulk of it done quickly is key? Or are you transcribing a legal deposition where every single word, pause, and utterance has to be captured perfectly?
The need for this kind of service is booming. The audio transcription software market is on track to hit around $2.5 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow by 15% each year through 2033. This isn't just a niche tool anymore; it’s become essential for everyone from media companies to universities and law firms.
AI vs Human Transcription
Let's break down the two main options. AI-powered tools are incredibly fast—they can often process an hour-long audio file in just a few minutes. This is a game-changer for content creators on a deadline, students trying to get lecture notes down, or anyone who just needs a solid draft now. If you're curious about how these systems work, our guide on AI-powered transcription software dives deeper into the technology.
The catch? Automated systems can get tripped up. Things like background noise, thick accents, or several people talking over each other can throw them off, leading to errors.
That's where manual transcription shines. Having a human professional listen and type out the audio guarantees the highest level of accuracy you can get. This is the only way to go for sensitive or complex files, like medical dictations, formal legal proceedings, or in-depth research interviews where every nuance matters. A human can easily parse overlapping sentences and figure out mumbled words in a way AI just can't yet.
To make this choice clearer, here’s a quick comparison:
AI vs Human Transcription: Which Is Right for You?
This table gives you a clear, side-by-side look at the strengths and weaknesses of automated and manual transcription to help you make an informed choice.
| Factor | AI Transcription | Human Transcription |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Extremely fast (minutes for an hour of audio) | Slower (hours or days, depending on length) |
| Accuracy | Generally 80-95%, lower with poor audio | 99% or higher, even with challenging audio |
| Cost | Very affordable, often priced per minute/hour | More expensive, priced per minute or by the hour |
| Best For | Clear, single-speaker audio, quick drafts, content creation | Legal, medical, complex interviews, final drafts |
| Weaknesses | Struggles with accents, noise, and multiple speakers | Higher cost and longer turnaround time |
Ultimately, the best choice depends entirely on your project's specific needs.
This decision tree helps visualize how your project's constraints—audio quality, timeline, and budget—naturally lead to one solution over the other.
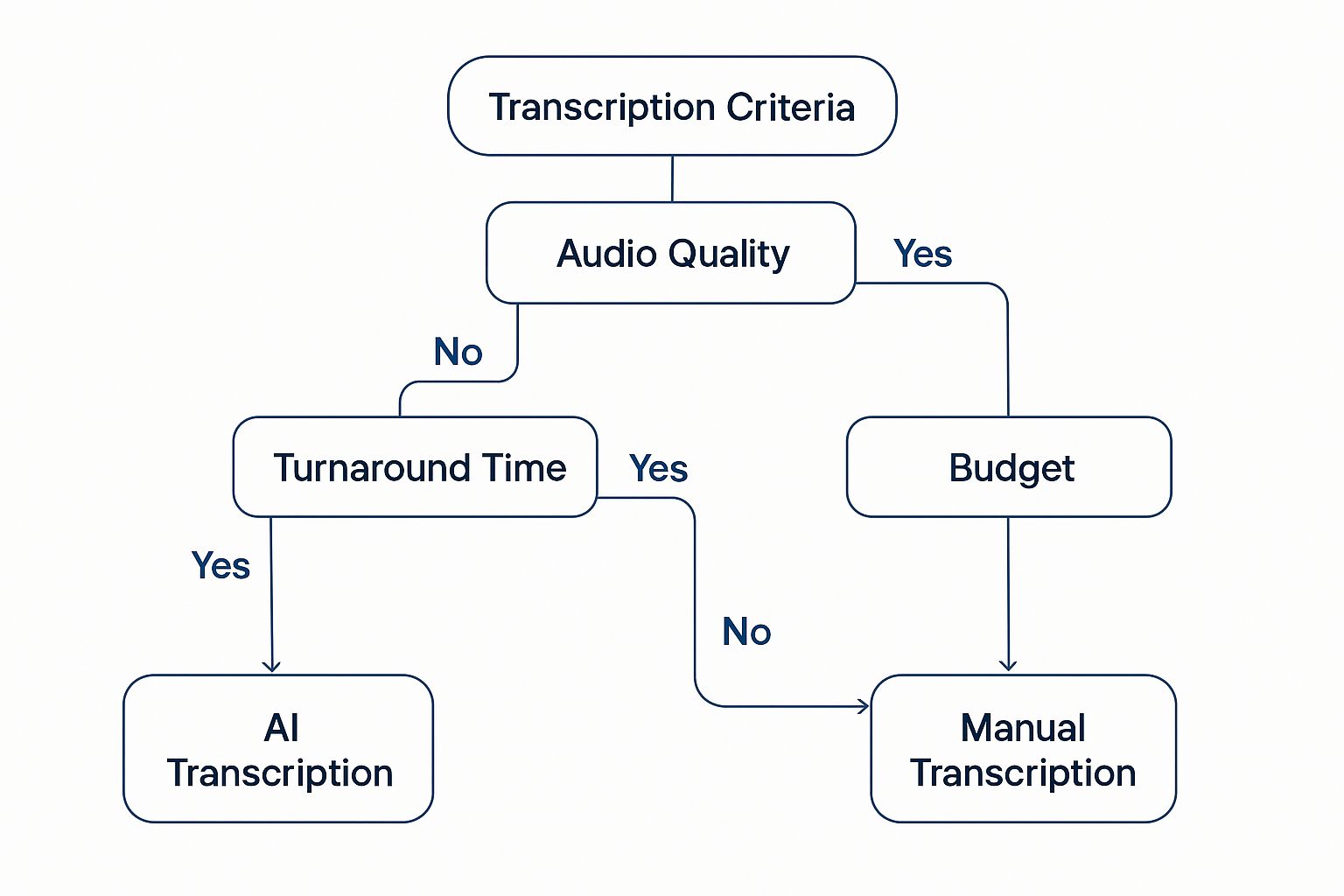
As you can see, if you have high-quality audio and speed is your top priority, AI is a fantastic starting point. But for projects where absolute precision is non-negotiable, the investment in time and money for a human transcriber is almost always worth it.
Prepping Your Audio for a Perfect Transcript
The final quality of any transcript hinges almost entirely on the clarity of the source audio. I like to think of it like building a house—if you start with a shaky foundation, the whole structure will be compromised. A few extra minutes spent cleaning up your audio file can genuinely save you hours of painful editing down the line.
This is especially true when you're dealing with dense legal depositions or complex medical consultations where every single word matters. The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" is the golden rule here. An AI transcription tool, no matter how advanced, can only work with what it hears. Muffled audio, background chatter, or speakers at wildly different volumes will trip up the AI and tank your accuracy.

Start at the Source
Honestly, the best way to guarantee a clean transcript is to start with a clean recording. It’s not always something you can control, but when you can, capturing high-quality audio from the get-go is the most powerful thing you can do.
This means being mindful of your recording space and the gear you're using. Something as simple as recording in a quiet, carpeted room without a lot of echo can make a world of difference. Your microphone and where you place it are just as critical. If you need some pointers, our guide on how to set up your microphone has some great, practical tips for getting crystal-clear sound. You'll find a lot of overlap with these best practices for video interview recording as well.
Your main goal should be achieving a high signal-to-noise ratio. It sounds technical, but it just means you want the speaker's voice (the signal) to be significantly louder than any background distractions (the noise).
Cleaning Up Imperfect Audio
But what happens when you’re handed a recording that’s far from perfect? All is not lost. You can still do a lot to improve it before uploading it for transcription, often with free and powerful tools like Audacity.
Here are a couple of common problems I see all the time and how to fix them:
- Pesky Background Noise: Got a constant low hum from an air conditioner or the buzz of an old office light? Audacity’s “Noise Reduction” effect is brilliant for this. It lets you isolate that unwanted sound and subtract it from the entire track, making the voices pop.
- Unbalanced Volume Levels: In interviews or meetings, you often have one person who speaks quietly and another who booms. This can confuse the AI. Using a "Compressor" or "Normalize" effect evens out these levels so the transcription engine can hear every participant clearly.
- The Right File Format: While MP3 is everywhere, it’s a “lossy” format. To shrink the file size, it discards some audio data forever. If you have the choice, always go with a lossless format like WAV or FLAC. It gives the AI the most information to work with, which directly translates to better accuracy.
Taking a moment for these prep steps feeds the transcription engine the cleanest possible data. The payoff is a much more accurate and useful document right from the start.
Turning Your Audio Into Text With an AI Transcription Tool
Alright, with your audio file prepped and polished, it's time for the fun part: letting the AI work its magic. This is where you really see the power of modern transcription—turning hours of audio into text in just a few minutes. Let's walk through how it typically works using a service like Whisperit as our example.
The tech behind these tools has come a long way. Thanks to some serious advancements in deep learning, today’s AI services can hit up to 99% accuracy under the right conditions. This isn't just a party trick; it's why industries from law to medicine are now leaning on AI for this kind of work. The precision is just that good.

This is what a typical dashboard looks like right after the AI has done its initial pass. You get the full text, complete with timestamps and speaker labels, ready for you to review.
Getting Around the Transcription Dashboard
First things first, you'll need to create an account and get a feel for the workspace. Most platforms, Whisperit included, make this super easy. Look for the big, obvious "Upload" button—you can usually drag and drop your file right onto the page.
Once you’ve uploaded your audio (again, a lossless format like WAV is your best bet), you'll see a few settings. Hang on a second before you hit that "Transcribe" button. Taking a moment to configure these options is the secret to getting a much cleaner first draft.
- Language Selection: This one is crucial. Make sure you tell the AI what language is being spoken. Even if it seems obvious, selecting the right one is the single most important step for accuracy.
- Speaker Identification: Does your recording have more than one person talking? If so, you'll want to turn on speaker identification (sometimes called "diarization"). The AI will automatically figure out who is speaking and label their lines, which saves a massive amount of editing time.
- Custom Vocabulary: Some of the more advanced tools let you upload a "cheat sheet" of words. This is incredibly useful for company names, industry jargon, or unique spellings of names. It gives the AI a heads-up on tricky terms.
After you’ve tweaked these settings, go ahead and kick off the transcription. You’ll be surprised at how fast it is—an hour-long audio file often takes just a few minutes.
What Else Is Out There?
While we're walking through the process with Whisperit, it's worth remembering there are a lot of great tools out there, each with its own perks. It's always a good idea to shop around and see what clicks for you. For instance, you could explore lunabloomai's AI transcription services to see how another platform handles the workflow.
The goal of using an AI tool isn't to get a perfect, publish-ready document on the first try. Instead, think of it as getting a 90% complete draft in 10% of the time, leaving you to focus on the final human polish.
Choosing the right platform often boils down to your specific needs. Some are built for team collaboration, while others might integrate better with video editing software. To help you sort through the options, we put together a guide on the https://www.whisperit.ai/blog/best-ai-transcription-software on the market. It’ll give you a solid overview and help you find the perfect fit for your projects.
Editing and Polishing Your First Draft
An AI-generated transcript gives you an incredible head start, but it's rarely a finished product. Even when Whisperit achieves 90-95% accuracy on a clean recording, you can bet there will be small errors. This is where your human touch comes in—turning a solid draft into a perfect, professional document.
Think of this step as more than just fixing typos. It's about making sure the final text truly captures what was said, all while being easy to read. The AI does the heavy lifting, but it’s that final polish that makes your transcript truly useful.

Developing an Efficient Editing Workflow
Diving into an edit without a system is a recipe for wasted time. I’ve found the most effective method is to listen to the original audio while reading the transcript. Whisperit, like most modern tools, has a playback feature that highlights the words as they're spoken, which makes spotting discrepancies a breeze.
Here’s a little pro tip: adjust the playback speed. Listening at 1.25x or 1.5x is usually the sweet spot. It's fast enough to be efficient but slow enough that you can still catch mistakes without losing the conversational context.
As you go through your first pass, keep an eye out for these common issues:
- Misheard Words: AI sometimes fumbles homophones (like "their" vs. "there") and almost always struggles with niche jargon or proper nouns. These are your top priority.
- Punctuation: The AI does a decent job with commas and periods, but it often misses the nuance of a question or an emphatic statement. Read for tone and adjust the punctuation to match.
- Speaker Labels: Always double-check that the dialogue is assigned to the right person. This gets tricky in recordings with multiple speakers, so it's a crucial checkpoint for interviews or meetings.
- Formatting: Tidy up any weird line breaks or paragraph spacing. A little formatting goes a long way in making the transcript readable.
Deciding Between Verbatim and Clean Read
While you're editing, you'll need to make a call on transcription style. This choice really boils down to what you're using the transcript for. Understanding the difference is a huge part of knowing how to transcribe an audio file properly.
Strict Verbatim This style is the "warts and all" approach. It captures everything exactly as it was spoken, including:
- Filler words ("um," "uh," "you know")
- Stutters and false starts
- Repeated words
- Non-verbal sounds like coughs or laughter
You’ll want a strict verbatim transcript for legal proceedings, academic research, or any situation where the way something was said is just as important as the words themselves. It’s the most complete and unfiltered record you can create.
Clean Read (or Edited Transcript) A clean read, on the other hand, tidies things up. It removes all the conversational clutter—the filler words, stutters, and repetitions—to present the speaker's ideas clearly. If you want a deeper dive, our guide on transcription tips for beginners explores these stylistic choices in more detail.
This is the go-to style for most business needs, like:
- Turning a podcast episode into a blog post
- Publishing meeting minutes for your team
- Creating clean, easy-to-read subtitles for a video
In the end, this editing phase is where you apply that final layer of human intelligence. By catching errors and choosing the right style, you’re crafting a document that isn’t just accurate but is perfectly suited for its intended purpose.
Tackling Tricky Transcription Challenges
Even with the best audio in the world, you’ll eventually hit a wall. Knowing how to transcribe an audio file isn't just about pressing "go"; it's about knowing what to do when things get messy. Heavy accents, industry jargon, and people talking over each other can turn a simple job into a real headache.
The good news? Most of these problems have surprisingly simple fixes. You don't need to be an audio engineer—you just need a few tricks up your sleeve. The need for accurate transcripts is only growing. In the U.S. alone, the transcription market ballooned to about $30.42 billion in 2024, and it's not slowing down. You can dig into more stats about the growing transcription market on grandviewresearch.com.
How to Handle Difficult Audio
Let's dive into some of the most common frustrations I see and how to get past them.
- Heavy Accents or Fast Talkers: If the AI is stumbling over a particular accent or someone is speaking a mile a minute, the playback speed controller is your best friend. I find that slowing the audio down to 0.75x speed during the editing phase makes it so much easier to catch those nuanced words the AI missed.
- Complex Technical Jargon: Got an audio file loaded with specialized terms, acronyms, or unique company names? This is exactly what Whisperit's custom vocabulary feature was built for. Before you even start, upload a simple list of these terms. This gives the AI a heads-up, and you'll see a massive improvement in accuracy right out of the gate.
- Multiple Overlapping Speakers: This is a classic problem. When voices overlap, AI transcription can turn into a jumbled mess. My go-to strategy here is to manually drop in timestamps—like
[00:15:32]—right where the confusion starts. This creates a bookmark, letting you jump straight to that moment in the audio to untangle who said what.
Remember, the final product isn't just a block of text; it's a usable document. Adding small bits of context, like timestamps or clarifying who's speaking, makes the transcript infinitely more valuable. This is especially true for legal or medical work where every detail matters.
And of course, when you're working with sensitive material, privacy is a top concern. We've put together a guide that walks you through exactly how to handle confidential information safely from start to finish.
Making these small adjustments can take a difficult transcription from a major roadblock to a minor speed bump, ensuring your final transcript is clean, accurate, and professional.
Your Top Transcription Questions, Answered
When you're just starting to figure out how to transcribe an audio file, you're bound to run into a few common questions. I see them come up all the time. Getting these sorted out early will save you a world of headache and help you get your project done right.
Let's dive into some of the big ones.
How Long Does It Really Take to Transcribe 1 Hour of Audio?
This is the million-dollar question, and the honest answer is: it depends. The gap between what an AI can do and what a human needs to do is massive.
- Using an AI service: For a clean, straightforward one-hour recording, an AI can spit out a draft in about 10-15 minutes. It’s astonishingly quick.
- Hiring a human transcriber: A seasoned pro will typically spend about four hours of work for every one hour of audio. That's the industry benchmark. If your audio is messy, has heavy accents, or is packed with technical terms, that ratio can easily climb.
- Doing it yourself (AI-assisted): Let's say you use AI to get a first pass and then clean it up yourself. For that same one-hour file, set aside anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours for editing. How long it takes really comes down to how accurate that initial AI transcript was.
The key thing to remember is that AI gives you incredible speed for that first draft. But the total time you'll spend is dictated by the audio's complexity and how perfect the final transcript needs to be.
What’s the Best Transcription Software to Use?
Honestly, there’s no single "best" tool for everyone. The right software depends entirely on what you're trying to accomplish. A podcaster who just needs some quick show notes has very different needs than a paralegal who needs a perfect record of a deposition.
If you just need speed and convenience, AI platforms are hard to beat. But if you're going the more traditional route, a lot of professionals swear by tools like Express Scribe, which lets you control playback with a foot pedal—a real game-changer. For those on a shoestring budget, you could even use the voice typing feature in Google Docs, but just know you’re signing up for a lot more manual editing.
My advice? Take advantage of the free trials offered by a few different AI services. It’s the fastest way to find out which one clicks with your workflow.
Can You Transcribe Audio with a Ton of Background Noise?
You can, but you probably won't like the results. Both AI algorithms and human ears will struggle, and you'll end up with a transcript full of mistakes and [inaudible] tags.
Your first line of defense is always to clean up the audio before you start transcribing. A free tool like Audacity has some great noise-reduction features that can make a huge difference.
An AI will give you a very rough draft from a noisy file. A human might be able to decipher more, but they’ll definitely charge you more for the extra effort. The best solution, without a doubt, is to get a clean recording from the get-go.
How Do I Keep My Sensitive Audio Files Confidential?
This is a critical concern, especially if you're dealing with legal, medical, or other private information. If you're handing your files over to a third-party service, you absolutely have to vet their security practices.
Dig into their privacy policy. Look for mentions of end-to-end encryption, and check if they're open to signing a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA).
For the highest possible level of security, the only truly airtight method is to do the transcription yourself, on a computer that's completely offline. It's more work, of course, but it completely eliminates any risk of a third-party data breach.
For legal teams who need both robust security and a workflow built for accuracy, Whisperit was designed to fill that gap. It combines powerful AI transcription with features specifically for confidential work—like Swiss/EU hosting and GDPR-aligned controls—so you can go from dictation to final document with total peace of mind.
You can learn more about how it works at https://whisperit.ai.