How to Implement Zero Trust Without the Headaches
Transitioning to a zero trust model is a serious undertaking, not just a technical refresh. It's a complete overhaul of your organization's security philosophy, moving away from the old, outdated "castle-and-moat" thinking.
That traditional approach, where anything inside the network was automatically trusted, just doesn't cut it anymore. With remote work, cloud services, and increasingly sophisticated threats, the network perimeter is no longer a physical boundary—it's everywhere.
Your Zero Trust Journey Starts with a Mindset Shift
This new reality demands a much tougher security stance. Forget 'trust but verify'. The mantra now is never trust, always verify. Every single access request, no matter where it comes from or who it's from, has to be treated as a potential threat until proven otherwise.
This fundamental mindset is the bedrock of a successful zero trust implementation. It's why, by 2025, an estimated 72% of enterprises will have adopted or be actively rolling out zero trust frameworks.
Before you even think about the technology, you need to get your stakeholders on board with the why. This means building a strong business case that leadership understands and that clearly lays out the benefits of making this shift.
A zero trust strategy isn't something you can just buy and install. It's a comprehensive approach that weaves together different technologies, policies, and processes to protect what matters most in a constantly changing threat environment.
The Core Pillars of a Zero Trust Architecture
So, how do you actually start building this out? It all begins with understanding the core pillars of zero trust. These principles are the foundation, working together to create a security posture that is both tough and flexible. For a deeper dive into the core concepts, you can check out our comprehensive guide on what zero trust security is.
The table below breaks down these fundamental pillars. Think of them as the non-negotiable building blocks of your entire strategy.
| Pillar | Description | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Verify Identities | Continuously authenticating and authorizing users based on all available data, not just a one-time login. This involves Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and behavioral analytics. | Ensures that the person accessing a resource is truly who they claim to be, stopping credential theft in its tracks. |
| Validate Device Health | Checking every device (laptop, phone, server) against security policies before granting access. This includes verifying software updates, endpoint protection, and the absence of malware. | Prevents compromised or non-compliant devices from connecting to your network and introducing threats. |
| Enforce Least-Privilege Access | Granting users and applications the absolute minimum level of access required to do their job—and nothing more. This is often achieved through techniques like micro-segmentation. | Drastically limits an attacker's ability to move laterally across the network if a single account or system is breached, containing the damage. |
By building your implementation around these three pillars, you ensure that every access decision is made intelligently and securely, based on real-time context rather than outdated assumptions of trust.
Defining Your Protect Surface

The very first move in any real-world zero trust implementation is to stop thinking about the old, sprawling network perimeter. It’s an outdated concept. Instead, your focus needs to shift inward to what truly matters—what we call the "protect surface."
This isn't your entire network. Far from it. The protect surface is a curated collection of your organization’s most critical Data, Applications, Assets, and Services (DAAS).
Trying to apply zero trust principles everywhere at once is a classic rookie mistake. You'll burn out your team, exhaust your budget, and ultimately fail. The whole point is to build a small, manageable, and highly secure perimeter around your most valuable assets, not boil the entire ocean. Getting this right from the start is foundational; it ensures you’re putting your best defenses where they'll make a real difference.
Identifying Your Critical Assets
To figure out what's in your protect surface, you first need a solid inventory of your DAAS. This isn't just a job for the IT team scanning the network. It requires getting out of your chair and talking to people across the entire organization to understand what they can't live without.
Start by asking the right questions to the right departments. The goal is to uncover the systems and data that are absolutely essential for business operations.
- Talk to Finance: "What systems hold sensitive financial records, like payroll, invoicing, or customer payment details?"
- Check with HR: "Where is all the employee personally identifiable information (PII) stored? Think social security numbers, home addresses, and bank details."
- Meet with Sales & Marketing: "Which CRM or database would bring everything to a halt if it went down?"
This collaborative approach is non-negotiable. An application that looks insignificant to the infrastructure team might be the single most important tool for the sales team. The end result of this discovery phase should be a prioritized list of what you absolutely cannot afford to have compromised.
Think of your protect surface as the crown jewels of your organization. Before you can design the vault, you first have to know exactly what treasures you're protecting and where they are.
Mapping the Transaction Flows
Once you know what you need to protect, the next step is figuring out how it's actually used day-to-day. This is where mapping transaction flows comes in. It's all about tracing the paths data takes and identifying how different users, devices, and applications interact with your critical assets.
Let’s take that critical customer database as an example. A salesperson might access it from their laptop over a coffee shop Wi-Fi. A marketing automation tool might connect to it via an API to send emails. And the finance team might pull reports from it using a desktop inside the office. Each of these is a completely different transaction flow.
Understanding these flows is everything. It tells you exactly who needs access, from where, and through which applications. This detailed map becomes the blueprint for your zero trust controls, allowing you to build incredibly granular policies that wrap security directly around the normal, legitimate pathways to your most sensitive data.
4. Architecting Your Zero Trust Controls
Alright, you've mapped your protect surface. Now for the fun part: building the security architecture that brings your Zero Trust strategy to life. This is where we stop talking theory and start designing the actual controls that will guard your most critical assets.
Forget about the old-school, single-firewall fortress. We're thinking differently. We're building intelligent, targeted microperimeters around each of those assets you just identified.
This means creating small, tightly controlled zones for individual parts of your protect surface—maybe a single application, a specific database, or a sensitive data repository. By shrinking the attack surface this way, you make it incredibly difficult for an attacker to move laterally. If one segment gets compromised, the blast radius is tiny.
It's like putting your crown jewels in separate, high-security vaults instead of one big, easy-to-crack room.
This diagram gives a great high-level view of how this process flows, from classifying your assets all the way to enforcing your new policies.
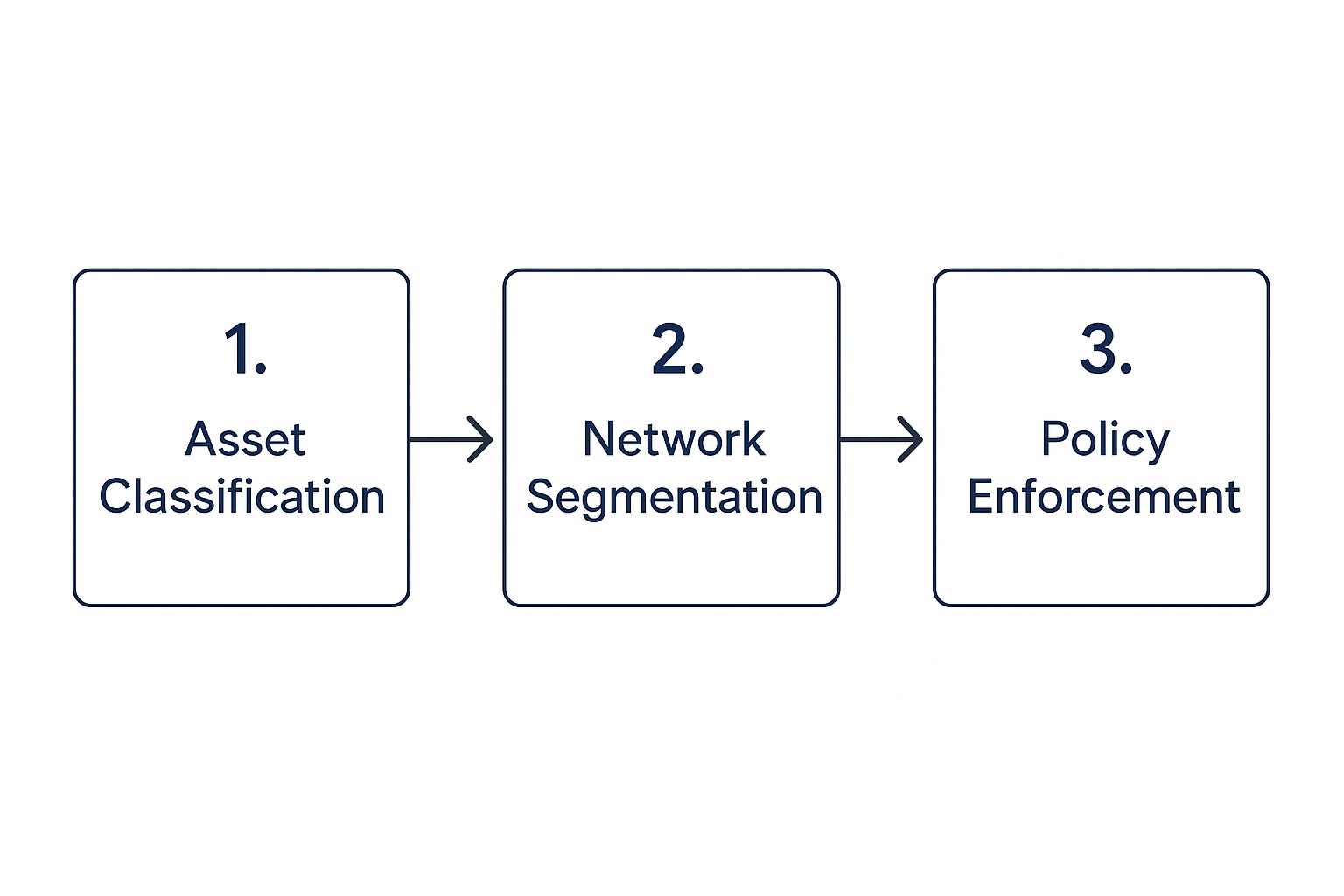
As you can see, each step builds on the last. This logical progression ensures your security controls are purpose-built to protect the specific assets they’re assigned to.
Creating Context-Aware Access Policies
The real magic of Zero Trust lies in its granular, context-aware policies. A segmentation gateway or a next-generation firewall acts as the bouncer for each microperimeter, but it needs a smart rulebook. This is where the Kipling Method comes in handy, forcing you to define access rules by answering a few key questions for every single request:
- Who is asking for access? (User identity, role)
- What application are they trying to use? (The specific resource)
- When is the request happening? (Time of day, day of the week)
- Where is the user connecting from? (Geolocation, network segment)
- Why do they need this access? (Business purpose, task context)
- How are they connecting? (Device type, health posture, OS version)
Using this framework, you naturally build policies based on the principle of least privilege. For instance, a policy might only allow a specific user from the finance team (who) to access the payroll system (what) during standard business hours (when) from a company-issued, patched laptop (how). Any request that doesn't tick all those boxes is automatically shut down.
The goal is to make access decisions dynamic and intelligent. We're no longer trusting someone just because they're on the "right" network. We trust them because the specific context of their request lines up perfectly with a highly specific, pre-approved policy.
The Technology That Makes It All Work
Pulling this off requires a modern technology stack. To get started, you'll need to map your Zero Trust principles to the right tools for the job.
Essential Zero Trust Technology Mapping
This table outlines the core Zero Trust principles and the technologies you'll need to implement them effectively.
| Zero Trust Principle | Core Technology | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Verify Explicitly | Identity and Access Management (IAM), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Authenticates and authorizes every user and device before granting access. |
| Use Least Privilege Access | Privileged Access Management (PAM), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Restricts user access rights to the bare minimum required for their job function. |
| Assume Breach | Microsegmentation, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Isolates network traffic and continuously monitors for threats to limit lateral movement. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), User/Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) | Collects and analyzes security data in real-time to detect anomalies and policy violations. |
As you can see, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the central nervous system of any Zero Trust architecture. It’s no wonder that 67% of organizations name IAM and data encryption as their top priorities when implementing these controls.
IAM platforms, especially when paired with strong Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), are what power the "who" part of the Kipling Method. They ensure every user is truly who they claim to be before their request even gets a look.
Ultimately, your architecture will weave these technologies together into a cohesive defense. But just deploying them isn’t the end of the story. You have to constantly validate that they’re working as intended. To dig deeper into that, check out our guide on how to test security controls—it’s a crucial piece of maintaining a strong Zero Trust posture over the long haul.
Rolling Out and Monitoring Your Framework
Let's be clear: implementing zero trust isn't a one-and-done project. There's no finish line. Think of it as a living, breathing part of your security culture that constantly needs to be refined. Trying to do a "big bang" rollout across the entire organization is a classic mistake and a surefire way to cause chaos.
The smarter move is a phased deployment. Start small. Pick a low-risk piece of your protect surface to experiment with. This could be a brand-new application that isn't business-critical or a small, tech-savvy team that can give you solid feedback without freaking out.
This pilot program becomes your real-world lab. It’s where you can test your policies, see how your controls actually work, and get honest feedback on the user experience before you even think about touching more critical systems. This methodical approach lets you iron out the wrinkles in a safe space.
Turning Data Into Actionable Intelligence
Visibility is everything in a zero trust world. If you can't see what's happening, you're just guessing. You need to be pulling telemetry from every single piece of your architecture—identity systems, endpoints, applications, segmentation gateways, you name it. This isn't just about collecting logs to check a compliance box; it's about understanding how people and systems are really interacting with your data.
A good Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is invaluable here. By centralizing all this data, you can start connecting the dots and asking the right questions:
- Are the access patterns what we expect? Is the finance team logging into the accounting app during normal business hours, or are we seeing weird login attempts at 3 AM from a country we don't operate in?
- Are any devices failing their health checks? Catching a non-compliant laptop before it connects to a sensitive resource is a massive win.
- Are we seeing a huge number of failed login attempts for one specific account? That's a huge red flag for either a brute-force attack or a compromised password.
This continuous feedback loop is where zero trust truly comes to life. It’s what shifts your security from a static set of rules to a dynamic system that can actually respond to threats.
The real goal here is to get away from periodic, once-a-year audits and move to continuous, real-time validation. In a mature zero trust environment, every single access request is a data point that helps you strengthen your security posture.
This visual really captures the cyclical nature of a zero trust model.

As the diagram shows, defining your protect surface is just the first step. The real, day-to-day work is in the monitoring and maintenance, constantly adapting to new threats and changing business needs.
Refining Policies Based on Real-World Activity
All that data you're collecting is useless if you don't do anything with it. The insights you gather from monitoring need to directly feed back into your access policies. For example, if you notice a marketing application is constantly trying to ping a database it has no business talking to, that’s your cue to tighten the microperimeter rules around it.
This process never really ends. You'll find yourself constantly tweaking controls, checking to see if your changes worked, and hunting for new potential gaps. This proactive, iterative approach is the only way to maintain a truly resilient security posture over the long haul.
Performing a regular security risk assessment gives you a structured way to handle this ongoing analysis, helping you decide which adjustments to prioritize based on their potential business impact.
In the end, monitoring is what closes the loop. It proves your architecture is working the way you designed it and gives you the intelligence you need to make it stronger every single day.
Overcoming Common Implementation Hurdles

Let's be realistic: moving to a zero trust model isn't a simple flip of a switch. It’s a major strategic shift, and you’re bound to hit a few bumps in the road. Knowing what these roadblocks look like ahead of time is the best defense against derailing your project.
One of the first walls teams usually hit is dealing with legacy systems. We've all got them—those older, on-premise servers and applications that were built long before anyone was talking about identity-aware security. They often lack the modern authentication protocols or API hooks needed to plug directly into a zero trust architecture.
The temptation might be to rip and replace, but that's a recipe for disaster. A much smarter play is phased integration. You can use tools like application proxies or segmentation gateways to essentially wrap a modern security blanket around these old assets. This lets you enforce zero trust policies without having to rewrite the core application, which is a massive win.
Gaining Organizational Buy-In
Getting the technology right is only half the puzzle. You also need to win over the people. A successful zero trust project demands a real cultural change, from the top floor all the way to the end-users who just want to get their work done. Most of the pushback you'll get comes from a simple fear of disruption or not understanding why this change is happening.
This is where clear communication becomes your most important tool. You need to frame this as a business enabler, not just another security lockdown.
- When talking to leadership: Ditch the technical jargon. Focus on reducing business risk and building resilience. Explain how zero trust is what allows the company to safely embrace remote work and move faster in the cloud.
- When talking to your users: Highlight what's in it for them. Let's face it, nobody loves connecting to a clunky old VPN. Explain how modern zero trust access is often faster and more seamless.
Nothing builds support faster than a successful pilot program. Pick a small, motivated team and show them how much better their workflow is. Once people see the benefits with their own eyes, that initial resistance starts to melt away.
A zero trust journey is as much about changing mindsets as it is about deploying technology. By clearly articulating the "why" behind the shift, you can build the momentum needed to overcome technical and cultural inertia.
Managing Costs and Resources Effectively
The practical side of things—money and people—can be just as challenging. It's no surprise that while 81% of organizations have started their zero trust journey, 48% point to cost and resource constraints as major roadblocks. The data, highlighted in research on the state of zero trust security, confirms that the investment required to move away from old security models is significant.
This is why a phased, risk-based approach is your best friend. Don't try to boil the ocean. Start by focusing your budget and team's energy on protecting your most critical assets—the crown jewels of your protect surface.
This strategy delivers a clear return on investment right out of the gate, which makes it much easier to get the budget you need for the next phase. It’s a methodical approach that also fits perfectly with formal security frameworks. For instance, if you're aiming for compliance, learning how to get ISO 27001 certified can provide a solid structure for documenting and managing your new zero trust controls.
Answering Your Questions About Zero Trust
Even with the best roadmap, shifting to a zero trust mindset is a big change, and it’s natural to have questions. This isn't just another piece of software; it's a fundamental change in how you approach security. Let's tackle some of the most common questions that pop up when organizations start down this path.
Our aim here is to cut through the noise and give you clear, practical answers to help you move forward with confidence.
Where on Earth Do I Start with Zero Trust?
The absolute first thing you need to do is define your "protect surface." This isn't about your entire network. Instead, it's about pinpointing the crown jewels: your most critical data, applications, assets, and services (DAAS).
Think about it this way: instead of trying to build an impenetrable wall around your entire property, you're starting by putting a vault around your most valuable possessions. This focus ensures you're applying security controls, like micro-perimeters, where they'll have the biggest impact right from the start.
Do I Need to Buy a Whole New Set of Tools?
Not necessarily, and that's a common misconception. Zero trust is a strategy, not a product. You can, and should, build on what you already have.
Your existing tools—like next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), Identity and Access Management (IAM) platforms, and endpoint security software—are often the perfect building blocks. The real work is in reconfiguring and integrating them to support zero trust principles, like strict least-privilege access and continuous verification. It's usually more of a strategic pivot than a costly "rip and replace" overhaul.
A lot of people think zero trust means throwing out their current security stack. The reality is much more practical. It’s about leveraging your existing investments in a smarter way to enforce a "never trust, always verify" policy across the board.
How Does This Work for All Our Remote Employees?
Zero trust is practically built for the modern remote and hybrid workforce. It completely demolishes the old, broken idea of a trusted "internal" network versus an untrusted "external" one.
For a remote employee, every single access request is treated as if it’s coming from an open, untrusted network—it doesn't matter if they're at home, in a coffee shop, or in the office next door.
Access to an application is granted one session at a time, and only after two things are confirmed:
- The user’s identity (usually with multi-factor authentication)
- The security health and posture of their device
This model ensures a stolen password or a compromised laptop doesn't become a skeleton key to your entire digital kingdom. It's a core concept for security in a world without perimeters and aligns with many of the ideas in our essential data security best practices guide.
Is This an All-or-Nothing Project?
Absolutely not. In fact, trying to do it all at once is a recipe for failure. The most successful zero trust journeys are phased and iterative.
Most teams start small. They pick one high-value area to focus on—like securing access to a critical cloud application or protecting a specific set of sensitive data.
This approach lets you score an early win, learn valuable lessons, and fine-tune your policies before you roll the model out to other parts of the business. It’s a far more manageable and budget-friendly way to make the transition.
Ready to secure your document workflows with the same level of diligence? Whisperit provides a cutting-edge AI dictation and editing platform with a strong focus on privacy and security. Trusted by professionals, our platform helps you complete documents up to two times faster while ensuring your data remains protected.
Learn more at https://whisperit.ai.