Encrypted File Transfer: Secure Ways to Protect Your Data
Encrypted file transfer is, at its heart, about protecting your information as it moves from one place to another. Imagine you're sending a sensitive contract through the mail. You wouldn't just stick it in a regular envelope for anyone to see, would you? Of course not. You'd place it in a locked briefcase that only the intended recipient has the key to open.
That’s exactly what encrypted file transfer does for your digital files. It’s your data's personal bodyguard, ensuring that what you send arrives safely and can only be seen by the right person.
What Is Encrypted File Transfer and Why It Matters

Technically speaking, encrypted file transfer is the process of converting your data into a complex, unreadable code—called ciphertext—before it travels across a network. Once it reaches its destination, it can only be unscrambled and read by someone who has the specific decryption key. This keeps the information secure both while it's moving (in transit) and while it's stored (at rest).
In today's business environment, this isn't just a nice-to-have; it's absolutely essential. Without strong encryption, sensitive information like financial records, customer details, and your company's intellectual property are sitting ducks. If a cybercriminal intercepts that data, it's completely exposed, which can lead to catastrophic data breaches.
The Growing Demand for Secure Transfers
The push for better security is more than just a trend—it’s a clear market reality. The global secure file transfer market is on a steep upward curve, projected to grow from USD 2.29 billion in 2023 to an estimated USD 5.08 billion by 2033. This surge shows just how central secure data exchange has become to modern business.
The Business-to-Business (B2B) sector is a huge part of this story, accounting for 42% of the market share in 2023. This highlights just how critical encrypted transfers are for maintaining secure partnerships and protecting complex supply chains.
For highly regulated sectors like Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), which held a 22% market share, encrypted file transfer is non-negotiable. The combination of strict compliance rules and the high value of financial data means every single transaction must be locked down tight.
A Quick Look at the Core Components
To truly grasp how encrypted file transfer works, it helps to break it down into its fundamental parts. Each component plays a specific role in creating a secure environment for your data.
Core Components of Encrypted File Transfer
| Component | Description | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | The process of converting readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext). | Scrambling a message into a secret code that only you and your friend know. |
| Authentication | Verifying the identity of the sender and receiver before any data is exchanged. | Showing your ID to a security guard before entering a secure building. |
| Integrity Checks | Ensuring the data hasn't been tampered with or corrupted during transfer. | Checking that the seal on a package is unbroken before you open it. |
| Audit Trails | Creating a detailed, time-stamped log of all file transfer activities. | A building's security camera footage that records everyone who enters and exits. |
These elements work together to form a complete security system that protects your files at every step.
Beyond Basic Protection
True security is about more than just hitting "send" on an encrypted file. It's about building a comprehensive security framework. To be truly effective, this system needs to cover every stage of your data's lifecycle, from creation to deletion.
When you bring together strong encryption, reliable authentication, and thorough integrity checks, you create a powerful defense against modern cyber threats. For anyone looking to improve their security posture, exploring methods for https://www.whisperit.ai/blog/encrypted-document-sharing is a fantastic place to start building a more resilient data protection strategy.
How Encryption Creates a Digital Fortress for Your Data

To build a truly secure system for encrypted file transfer, you have to defend your data on two distinct battlefronts. First, you need to protect it while it's actively moving across a network—this is known as protecting data in transit. Then, you have to secure it once it's stored on a server or hard drive, which is called protecting data at rest.
Think of it this way: protecting data in transit is like putting your valuables inside a heavily guarded armored truck for a cross-country trip. Protecting data at rest is like locking that same cargo inside a fortified bank vault once it arrives. Both are absolutely critical. A weakness in either one undermines the entire security process.
At the heart of this digital fortress are two core encryption methods that work together, creating a seamless shield for your information.
Understanding Symmetric Encryption
The first method is symmetric encryption, which is the more straightforward of the two. It uses a single, secret key to both lock (encrypt) and unlock (decrypt) a file.
Imagine you have a diary with a unique physical key. You use that key to lock it, and a trusted friend uses an identical copy to open it. As long as only the two of you have that key, the diary’s contents stay completely private.
That’s essentially how symmetric encryption works. Its main advantage is pure speed and efficiency, making it perfect for encrypting large files or big batches of data in a hurry. The real challenge, however, is securely sharing that single key with the recipient without someone else intercepting it. If the key is compromised, the file's security is gone.
The Power of Asymmetric Encryption
This is where asymmetric encryption steps in. Instead of one shared key, this method gives every user a pair of mathematically linked keys: a public key and a private key.
- Public Key: Think of this as your own personal, secure drop-box slot. You can share it with anyone, and they can use it to encrypt a file to send to you. The key can only lock data; it can’t unlock it.
- Private Key: This is the only thing that can open your drop-box. You must keep it completely secret, as it's the only key capable of decrypting files that were locked with your public key.
This two-key system elegantly solves the key-sharing problem. A sender can use the recipient’s public key to encrypt a file, knowing with certainty that only the recipient, holding their unique private key, can ever access it.
How These Methods Work Together
In most modern encrypted file transfer systems, these two methods are combined to get the best of both worlds. The process usually unfolds like this:
- Generate a Session Key: The system creates a brand-new, one-time symmetric key just to encrypt the actual file. This is done because symmetric encryption is much faster for large amounts of data.
- Encrypt the Session Key: The system then takes that new symmetric key and encrypts it using the recipient's public key (asymmetric encryption). This protects the key itself while it's in transit.
- Transfer the Data: The encrypted file and the encrypted symmetric key are both sent to the recipient.
- Decrypt and Access: The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the symmetric session key. Once they have the session key, they can use it to quickly unlock the main file.
This hybrid approach pairs the speed of symmetric encryption with the superior security of asymmetric key exchange, creating a process that is both fast and incredibly secure.
This layered approach is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct sequence of private keys, forming the bedrock of a trusted digital environment. To learn more about building this type of robust framework, you can find a wealth of information in our complete guide to Whisperit's security architecture.
To see how these concepts translate into action, you can explore a checklist for implementing data encryption. This combination of strong encryption standards is what allows an encrypted file transfer solution to provide true end-to-end protection for your most valuable information.
Choosing the Right Secure Transfer Protocol
Picking the right method for an encrypted file transfer feels a lot like choosing the right vehicle for a journey. A sleek sports car is great for a fast highway trip, a rugged truck is built for tough off-road terrain, and a reliable sedan is perfect for everyday commuting. Each gets you where you need to go, but their suitability hinges entirely on the specifics of your trip.
In the same way, the world of secure file transfer has several options, each with its own history, strengths, and best-fit scenarios. While they all share the goal of protecting your data, they get the job done in fundamentally different ways. The three you'll run into most often are SFTP, FTPS, and HTTPS. Getting a handle on their differences is the key to building a security strategy that's both strong and sensible for your organization. To make the best choice, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of understanding network protocols for enhanced security.
SFTP: The Automation Workhorse
First up is SFTP, which stands for SSH File Transfer Protocol. This is the modern go-to for automated, high-volume file transfers. It works over a single, secure channel, relying on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol to authenticate both the sender and receiver and to encrypt absolutely everything—the data, the commands, all of it.
Think of SFTP as an armored train running on a dedicated, private track. The engine, the cargo cars, and the conductor's instructions are all protected inside one secure tunnel. This single-port operation makes it incredibly easy for firewalls to handle and a breeze for network administrators to manage.
Thanks to its rock-solid reliability and strong authentication using SSH keys, SFTP has become the top choice for:
- Automated server-to-server data syncing.
- Systematic batch processing of financial or operational data.
- Integrating with enterprise applications that need regular, secure data feeds.
FTPS: The Modernized Classic
Next, we have FTPS, or FTP over SSL/TLS. This protocol takes the original File Transfer Protocol (FTP)—a technology that’s been around since the early days of the internet—and bolts on modern SSL/TLS encryption. That’s the very same security technology that protects your online banking and shopping.
Imagine adding a heavily armored escort to a classic, reliable cargo truck. The truck itself is based on older tech, but the escort provides the robust security you need. The catch? FTPS requires two separate channels: one for commands and another for the data itself. This can sometimes cause headaches with firewalls, which might need special configurations to let both connections through. Still, FTPS remains a solid option for businesses that have legacy systems built around FTP but need to add a modern layer of security.
HTTPS: The Universal Standard
Finally, there’s HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). Most of us know it as the little padlock icon in our web browser, but it’s also a powerful protocol for file transfers. Every time you upload a document to a secure web portal or download a report from your online banking site, you’re using HTTPS.
It’s the all-purpose vehicle of secure transfers—it's versatile, universally supported by every web browser, and incredibly simple for end-users. No special software is needed. Its main strength is in user-driven, manual file exchanges through a web interface, making it perfect for customer-facing applications and secure document portals.
This infographic helps break down the core encryption technologies that make these protocols secure.
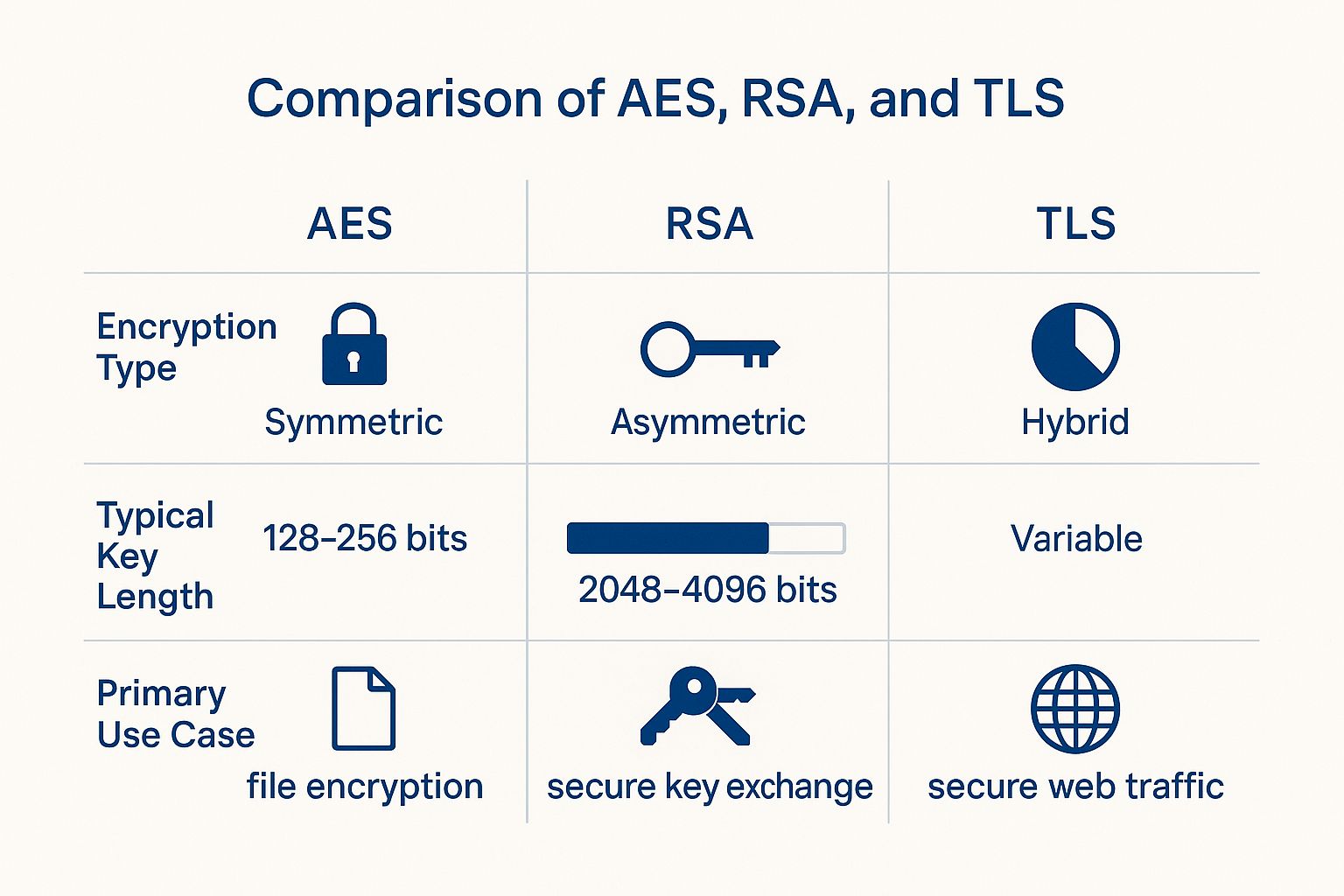
The image really shows how different encryption types—symmetric, asymmetric, and hybrid—are each specialized for different jobs, from locking down a single file to securing an entire communication channel.
The global shift to remote work and digital operations has put these technologies in the spotlight. In fact, the secure file transfer market is projected to shoot past $3 billion by 2025, growing at an impressive CAGR of about 10% from 2020 to 2025. This surge shows just how critical secure data exchange has become for organizations everywhere.
Making The Right Choice For Your Needs
When it comes down to SFTP vs. FTPS vs. HTTPS, the question isn't "Which one is best?" but rather, "Which one is best for this specific task?"
To help you decide, let's put them side-by-side and compare what really matters.
SFTP vs. FTPS vs. HTTPS Protocol Comparison
| Feature | SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) | FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) | HTTPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Foundation | SSH (Secure Shell) | SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) | SSL/TLS |
| Connection | Single secure connection on one port. | Two connections (command and data channels). | Single connection, handled by the web browser. |
| Firewall Friendliness | Excellent. Only one port needs to be opened. | Can be complex. May require a range of open ports. | Excellent. Uses the standard web port (443). |
| Ideal Use Case | Automated, server-to-server transfers. | Securing legacy FTP workflows. | User-facing web uploads and downloads. |
Ultimately, a truly comprehensive encrypted file transfer strategy might not pick just one. Instead, it could involve using all three protocols for different purposes. You might use SFTP for your backend data processing, FTPS to connect with a partner’s legacy system, and HTTPS for your customer-facing web portal.
Meeting Compliance Demands with Secure Transfers

In today's business world, technology isn't just about cool features—it’s about meeting non-negotiable operational needs. An encrypted file transfer is a perfect example of this. It's far more than just a security tool; it's a foundational requirement for any business that needs to comply with the strict regulations governing sensitive data.
Ignoring these standards isn't a simple IT oversight. The consequences can be devastating, from crippling fines and legal action to a permanent loss of customer trust. For any organization that handles personal, financial, or health data, solid encryption is the price of admission for operating legally and protecting your reputation. This reality changes the conversation from a technical "how" to a business-critical "why."
The High Stakes of Industry Regulations
Different industries operate under specific rulebooks designed to protect consumer data. These regulations aren't suggestions—they have the full force of law, and encrypted file transfers are almost always a central piece of the compliance puzzle.
Let’s break down the big ones.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): In healthcare, nothing is more important than patient confidentiality. A hospital sending records to a specialist or a lab sharing diagnostic images must ensure that Protected Health Information (ePHI) is unreadable to unauthorized parties. An encrypted transfer is the digital equivalent of a sealed, tamper-proof courier, making it essential for meeting HIPAA’s stringent security rules.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This affects any business that deals with the data of EU citizens. GDPR demands that personal data be processed securely. Sending a customer list to a marketing partner without end-to-end encryption is a clear violation, one that could lead to fines of up to 4% of your company's annual global turnover.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): For any e-commerce store, retailer, or service provider handling credit card payments, PCI DSS is the law. It dictates that cardholder data must be protected everywhere—both when it's stored (at rest) and when it's being sent (in transit). Using an encrypted file transfer to send batch transaction data to a payment processor is a baseline requirement.
These regulations send a clear message: if your business handles sensitive data, you are legally obligated to protect it. Encryption isn't just a good idea; it's the prescribed method for guaranteeing data privacy and integrity, forming the backbone of any serious compliance strategy.
From Compliance Checkbox to Business Advantage
While staying compliant might feel like a purely defensive game, it actually creates some powerful business advantages. A solid encrypted file transfer strategy shows a real commitment to protecting data, and that's a huge differentiator in today's market. When customers feel confident their information is safe with you, their trust deepens, paving the way for stronger relationships and loyalty.
For businesses trying to get their arms around these complex rules, a full understanding of data privacy compliance is key to building a resilient operation. By proactively embracing strong encryption, you can turn a regulatory headache into a genuine strategic asset.
Ultimately, choosing a reliable encrypted file transfer solution is a decision to build your business on a foundation of trust. It proves to regulators, partners, and customers that you take security seriously, helping you sidestep massive penalties and secure your reputation as a responsible leader in your field.
Implementing a Bulletproof File Transfer Strategy
Understanding the theory behind encrypted file transfers is the easy part. The real challenge? Turning that theory into a practical, rock-solid strategy that actually works for your organization. This is where you move beyond concepts and start making critical decisions about your infrastructure, access policies, and how you'll hold people accountable.
One of the first forks in the road is deciding between a cloud-based service or an on-premise solution. Going the on-premise route gives you complete control over your hardware and data, but it also means you’re on the hook for all the upfront costs, maintenance, and security updates. Cloud solutions, on the other hand, offer incredible scalability and are much easier to get started with, as the vendor handles all the heavy lifting on the backend. The right choice really boils down to your budget, in-house technical chops, and specific compliance needs.
This isn't just a niche concern; the demand for dependable file transfer solutions is surging. The global market was valued at $2.35 billion in 2024** and is projected to climb to **$2.51 billion in 2025. Looking ahead, experts see it hitting $3.63 billion by 2029, largely thanks to advancements like AI-driven threat detection and the adoption of zero-trust security models.
Core Pillars of an Effective Strategy
Whether you choose a cloud or on-premise system, a few foundational principles are absolutely non-negotiable. Think of these as the bedrock of any resilient and defensible security setup.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Let's be honest—passwords alone just don't cut it anymore. MFA adds a vital security blanket by requiring at least two forms of verification, dramatically cutting the risk of a breach even if a password gets stolen.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): The concept is simple but incredibly effective. Only give people access to the specific files and systems they absolutely need to do their jobs. Nothing more. For instance, a junior marketing associate has no business accessing sensitive C-suite financial documents.
- Maintain Detailed Audit Logs: Your system needs to be a meticulous record-keeper. It must log every single action: who touched a file, when they did it, what they did with it, and where it went. These logs are gold when you need to troubleshoot a problem, prepare for a security audit, or provide proof during a compliance check.
By layering these pillars, you move from a passive security stance to an active one. It’s a defense-in-depth approach where access is meticulously controlled and every single action is tracked and accounted for.
Integrating Security into Your Workflow
Putting these measures in place isn't a "set it and forget it" task. To be effective, security has to be woven into the fabric of your daily operations. A huge piece of this puzzle is continuous user training and awareness—your team needs to understand why these protocols matter and their personal role in safeguarding company data.
A truly comprehensive strategy also means looking at the bigger picture. After all, securing the transfer is just one part of the data lifecycle. For a broader perspective, this guide to secure file storage and transfers provides some excellent insights.
Furthermore, your secure transfer tool can't live on an island. It needs to play nicely with your wider security ecosystem, including your identity management and data loss prevention systems. For those handling a high volume of paperwork, our guide to effective document management security offers complementary strategies. When everything is integrated, your encrypted file transfer protocol becomes a strong link in your overall security chain, not just an isolated component.
Answering Your Top Questions About Encrypted File Transfer
Even when you've got the basics down, a few practical questions always pop up when it's time to actually put a secure file transfer system in place. Let's clear up some of the common points of confusion we hear from clients. Getting these answers straight will help you move forward with confidence.
So, what's the real difference between a password-protected file and a truly encrypted one? Think of it this way: a password on a zip file is like a simple lock on an office door. It keeps honest people out, but it's not going to stop someone determined.
True encryption, on the other hand, is like putting that file inside a bank vault. It's a completely different level of security, designed to withstand serious attempts to breach it.
Another question we get all the time is about using consumer-grade apps like Dropbox or Google Drive for business. They're easy and familiar, but are they safe enough? For personal photos, sure. But for sensitive business data, they often fall short. Their standard security models typically lack the strict access controls, comprehensive audit trails, and true end-to-end encryption required to comply with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
Where Should a Small Business Start?
If you're a small business owner, this can all feel a bit much. The best place to begin is with a simple data audit. You can't protect what you don't know you have. Figure out what sensitive data you handle—client lists, financial details, employee records—and get a clear picture of where it lives and how it moves.
Once you have that map, you can take a few concrete steps:
- Write It Down: Create a straightforward policy for handling and sharing company data. Keep it simple so people will actually follow it.
- Pick Your Tool: Find a dedicated secure file transfer solution. The non-negotiables are end-to-end encryption and detailed audit logs.
- Train Your People: Make sure everyone on your team understands the policy and knows how to use the new software correctly.
A common pitfall is thinking encryption is a magic bullet. The truth is, the technology is only one piece of the puzzle. Real security comes from the entire process—who has access, how encryption keys are managed, and whether you're keeping good logs.
Building a secure workflow is just as important as the tool you choose. To get a better handle on creating a solid framework, it's worth reviewing fundamental data security best practices. These principles offer a clear roadmap for creating a security posture that's both functional and easy to defend.
Taking these small, deliberate actions builds a surprisingly strong foundation. By getting answers to these questions and putting simple policies in place, any business, no matter the size, can dramatically improve its security and keep its most valuable information safe.
Ready to stop worrying about data security and start focusing on your work? Whisperit provides end-to-end encrypted dictation and document management, hosted securely in Switzerland. See how Whisperit can protect your sensitive information and boost your productivity today.