Document Management Security Strategies That Protect
Understanding Today's Document Security Landscape
The way businesses manage documents has changed drastically. While digital transformation has brought about greater efficiency and collaboration, it has also created new security risks. Many organizations that once felt secure with traditional methods now find themselves unprepared for the modern threat landscape. This raises a critical question: what distinguishes organizations with strong document security from those vulnerable to breaches?
The Current State of Document Security
A key difference lies in the adoption of modern document management systems (DMS). These systems offer essential security features like access control, encryption, and audit trails to protect sensitive data. However, a worrying number of companies haven't kept up with this technological advancement. The increase in remote work, for instance, has accelerated the need for robust DMS, yet many organizations remain exposed. A 2024 report revealed that nearly 40% of companies still depend on outdated systems lacking these advanced security features. This leaves them susceptible to unauthorized access and data leaks. Find more detailed statistics here This underscores a significant vulnerability in many organizations' security setups.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
Beyond outdated systems, the evolving nature of emerging threats demands constant vigilance. Increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, combined with the rise of insider threats, call for a more proactive approach to document security. Think of it as locking your front door – a necessary basic step, but not enough to deter a determined intruder. Likewise, simple password protection is no longer sufficient. Organizations must implement multi-layered security measures, including multi-factor authentication and data loss prevention tools, to effectively protect sensitive documents.
Building a Robust Security Foundation
The sheer volume of digital documents created and shared daily presents another significant hurdle. Managing this influx of data requires a clear strategy for organizing, classifying, and controlling access to documents. A comprehensive document management security strategy considers the entire document lifecycle, from creation and storage to archiving and eventual deletion. This makes security not just an IT responsibility, but a business-wide imperative requiring employee training and well-defined policies.
Understanding today's document security landscape is crucial for identifying specific vulnerabilities and developing effective mitigation strategies. By acknowledging these challenges and adopting a proactive security approach, businesses can protect their valuable information and ensure continuity in today’s dynamic environment.
Security Vulnerabilities That Actually Matter

Protecting sensitive documents requires a deep understanding of the vulnerabilities that lead to breaches. It's about moving beyond basic cybersecurity and creating a robust strategy. This means addressing the specific weak points that cybercriminals target. Let's explore these often-overlooked vulnerabilities and why conventional approaches might fall short.
Beyond Passwords and Basic Protection
While essential, basic password protection isn't enough. It's like locking your front door but leaving a window open. Even with a strong password, unauthorized access can happen through methods like phishing attacks, malware, or compromised devices.
This is where multi-factor authentication (MFA) becomes vital. MFA adds layers of security, requiring multiple verification forms. This significantly reduces unauthorized access risk, even if passwords are compromised. For more information on strengthening your data security, you can explore best practices in this article: How to master data security best practices
The Weakness Within: Insider Threats
A significant vulnerability often comes from within: insider threats. These range from negligent employees accidentally sharing sensitive data to malicious actors intentionally stealing it.
Strong access control is crucial. Role-based permissions and activity monitoring are key. These controls ensure people access only necessary information, limiting damage from accidental or intentional breaches.
Cloud Storage Mishaps: A Growing Concern
As cloud storage use increases, misconfigurations and improper access controls become major breach sources. A publicly accessible cloud storage bucket, for instance, can expose sensitive documents.
Carefully managing cloud permissions and regularly auditing access controls is critical. Despite the rise of electronic document management systems (EDMS), breaches persist. In fact, 60% of organizations experienced a document-related security breach in the past two years. This highlights vulnerabilities in storage, access control, and audit logging. To learn more about the trends and challenges in document management systems, explore this topic further.
Email Attachments: A Persistent Risk
Even seemingly harmless email attachments can be dangerous. Malicious attachments may contain malware that compromises systems, giving attackers access to sensitive documents.
Robust email security solutions are essential. This includes attachment scanning and filtering. Employee training on identifying and avoiding suspicious emails is also vital.
Addressing these vulnerabilities requires a proactive, multi-faceted approach. It involves implementing proper security measures, educating employees, and continuously monitoring systems for suspicious activity. By understanding the real risks, organizations can build effective document management security programs and protect their valuable information.
Building Security That Works In Practice
Document management security isn't just a theoretical concept; it's about developing practical solutions for real-world business situations. It's about striking a balance between strong protection and efficient workflows so your team can stay productive without jeopardizing sensitive data. This requires a strategic approach, learning from organizations that have effectively put these practices into action.
Practical Strategies for Effective Document Management Security
Effective document management security involves several key strategies:
- Conducting Meaningful Security Assessments: This means going beyond basic checklists and thoroughly investigating potential weaknesses. Like a building inspector who assesses the entire structure, a thorough security assessment analyzes every part of your document management system.
- Establishing Policies People Actually Follow: Security policies are useless if they're ignored. Policies must be clear, concise, and easy to understand and follow. Think of them like traffic laws – effective only when understood and obeyed.
- Implementing Layered Controls: Just as a single lock isn't enough to protect valuable assets, a layered security approach combines multiple controls for comprehensive protection. This could include access control, encryption, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools working together. For more detail on efficient workflows and security, see our guide on How to master document workflow management.
Benefits of Secure Document Management
The infographic below highlights the key advantages of robust document management security.
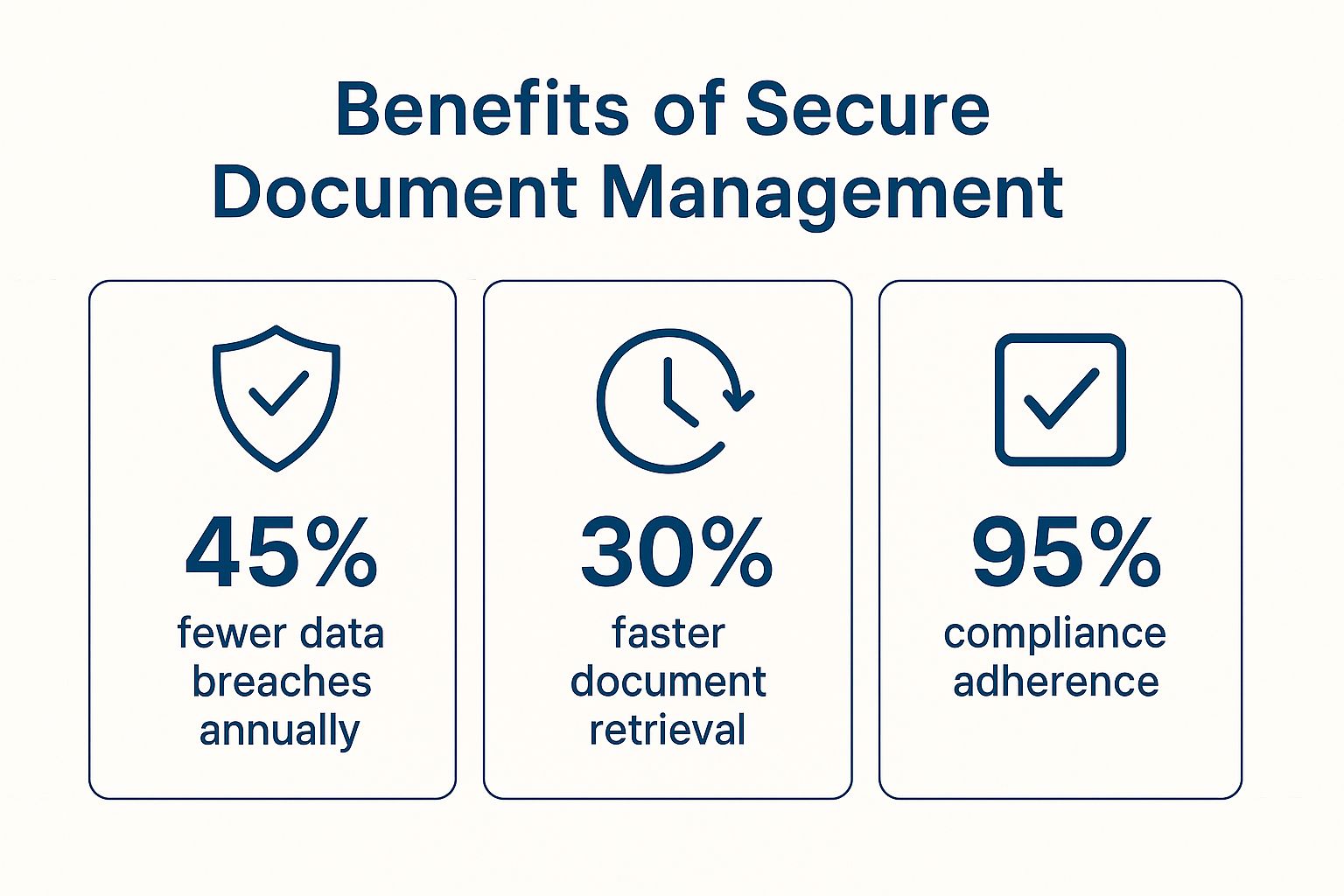
As shown above, organizations with strong document security experience 45% fewer data breaches each year, avoiding the high costs of data loss and reputational damage. Efficient document management practices also lead to 30% faster document retrieval, improving productivity and streamlining workflows. Finally, robust security contributes to 95% compliance adherence, reducing the risk of legal penalties and fines.
To further illustrate the components of a strong document security framework, the following table outlines implementation priorities and key features.
Document Security Framework Components
| Security Component | Purpose | Implementation Priority | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Restricting access to sensitive documents | High | User authentication, role-based permissions, audit trails |
| Encryption | Protecting data confidentiality | High | Data encryption at rest and in transit, key management |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization | Medium | Content inspection, policy enforcement, incident response |
| Security Awareness Training | Educating employees about security best practices | High | Regular training, phishing simulations, policy updates |
| Vulnerability Management | Identifying and mitigating security weaknesses | Medium | Regular vulnerability scanning, penetration testing |
| Incident Response Plan | Defining procedures for handling security incidents | High | Incident reporting, investigation, containment, and recovery |
This table summarizes the core elements of a comprehensive document security framework. Prioritizing access control, encryption, security awareness training, and incident response is crucial for establishing a strong foundation.
Learning from Security Leaders
The best document security programs are built on practical experience. By studying the methods of security leaders, we can identify key strategies that work in real-world settings. This involves understanding how they perform security assessments, develop effective policies, and implement layered controls that adapt to business growth while maintaining robust protection for sensitive information. These insights provide a valuable guide for building your own robust document management security program.
Access Control Beyond Basic Passwords

Simple password protection isn't enough for robust document management security. It's similar to locking your front door while leaving all the windows open. To truly safeguard sensitive information, modern authentication strategies are crucial. This means moving beyond simple passwords and embracing a multi-layered security approach.
Modern Authentication Strategies
Several key strategies form the core of modern document access control:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC allows access based on an individual's role within an organization. This ensures that users can only access documents relevant to their job responsibilities. For instance, a marketing team member wouldn't have access to sensitive financial records.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds extra layers of security by requiring multiple verification factors, not just a password. These could include a one-time code sent to a mobile device or biometric verification. Even if a password is compromised, MFA makes unauthorized access significantly more difficult.
- Zero Trust Security: The zero-trust model operates on the principle that no user or device should be inherently trusted, even within the organization's network. This approach mandates verification for every access attempt, minimizing the impact of potential security breaches.
Granular Permissions and Scalability
Effective access control requires granular permissions. This enables administrators to define precisely who can view, edit, or share specific documents. This level of control is essential for balancing security with necessary collaboration. Such nuanced access control prevents oversharing while ensuring authorized personnel can access the information they need. For a deeper dive into secure document sharing, check out this article: Encrypted Document Sharing Best Practices.
Furthermore, access control systems must be scalable. As organizations expand, their access control policies must adapt efficiently. Leading organizations build flexible access structures, maintaining strong security as the volume of users and documents grows.
Emerging Authentication Technologies
The field of authentication is constantly evolving. Biometric authentication, behavioral biometrics, and passwordless logins are gaining traction, changing how we secure sensitive documents. These technologies improve both security and user experience by streamlining access without compromising protection. These advancements represent the future of document management security, offering more robust and user-friendly alternatives to traditional passwords.
Encryption Strategies That Deliver Results
Encryption forms the bedrock of secure document management. It acts as the final safeguard, protecting sensitive information even when other security measures fall short. But simply encrypting documents isn't a guarantee of protection. The true strength of your security posture lies in selecting the right encryption method and implementing it strategically. This means considering your organization's specific needs and the types of documents you handle.
Key Management and Encryption Standards
Effective encryption relies heavily on robust key management. This involves the secure generation, storage, and distribution of encryption keys. Much like the physical key to a safe, these digital keys must be protected to prevent unauthorized access. For a deeper understanding of secure key handling, explore our article on encrypted document sharing. Strong access control is also paramount. Implementing robust security measures, such as those outlined in resources on access control and data security for Apache Druid, becomes essential for protecting sensitive data.
Furthermore, adhering to established encryption standards, like the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), is crucial. These standards have undergone extensive testing and are widely recognized for their strength. Using compliant methods also helps organizations meet regulatory requirements.
Different Types of Encryption: End-to-End, At-Rest, and In-Transit
A comprehensive encryption strategy must address data security across all stages of its lifecycle. This involves employing different encryption methods for various scenarios:
- End-to-End Encryption: This method ensures data is encrypted on the sender's device and decrypted only on the recipient's device. This protects data even if it's intercepted during transmission.
- At-Rest Encryption: Data stored on servers and other storage devices is encrypted with this approach. This protects data even if the physical storage is compromised.
- In-Transit Encryption: This safeguards data as it travels across networks. This is particularly important for documents shared via email or online platforms.
Maintaining Data Integrity and Balancing Security with Performance
One of the biggest challenges is implementing strong encryption without impacting performance. Organizations need to choose encryption methods that provide robust security without significantly slowing down data access or processing. This often involves finding the right balance between security levels and the computational demands of encryption.
Maintaining the integrity of encrypted data over time is also crucial. As technology advances, older encryption methods can become vulnerable. Organizations must regularly review and update their encryption strategies to maintain strong protection. This proactive approach ensures your document security stays ahead of emerging threats.
To help illustrate the different strengths and weaknesses of various encryption methods, we've compiled the following comparison table:
Encryption Methods Comparison: Comparison of different encryption approaches for document management with use case recommendations
| Encryption Type | Security Level | Performance Impact | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| AES-256 | High | Low | Sensitive documents, regulatory compliance |
| RSA | High | Moderate | Secure communication, digital signatures |
| Twofish | High | Low | Data at rest, file encryption |
This table summarizes some common encryption methods and their characteristics. As you can see, each method offers a different balance of security and performance. Choosing the right one depends on the specific requirements of your organization. By carefully considering these factors, you can implement robust encryption that safeguards your sensitive documents without compromising productivity.
Compliance That Goes Beyond Checkboxes

Regulatory compliance for document management security doesn't have to feel overwhelming. Instead of treating compliance as a checklist, view it as a chance to strengthen your overall security. By examining organizations successfully adhering to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX, we can create practical strategies that go above and beyond the bare minimum. This transforms compliance from a chore into a true competitive edge. For more insights, explore this helpful resource: How to master data security compliance.
Implementing Effective Audit Trails, Retention Policies, and Deletion Procedures
Audit trails are essential for robust compliance. They create a chronological record of every document access and modification, providing vital evidence in case of security incidents or audits. They act like a security camera for your documents, tracking who accessed what, and when.
Clear retention policies determine how long different document types must be stored. Alongside this, secure deletion procedures ensure sensitive data is permanently removed when it's no longer needed. This combination of tracking, retention, and deletion reinforces compliance and boosts overall document management security.
Turning Compliance into a Competitive Advantage
Top-performing organizations see compliance requirements as opportunities for operational improvement. For instance, the robust document security controls needed for GDPR compliance can also build customer trust and streamline internal processes. This illustrates how compliance isn't just about avoiding penalties – it's about building a more resilient and efficient business.
Staying Ahead of Evolving Regulatory Expectations
Regulatory environments are always changing. Staying up-to-date on new and emerging regulations is vital for maintaining long-term compliance. This requires proactively adapting document management security to meet changing requirements.
By anticipating future regulatory changes, organizations can avoid expensive last-minute adjustments and stay ahead of the curve. This proactive approach allows them to continually adapt their document management security strategies and maintain a leadership position in data protection. It fosters trust with customers and ensures ongoing regulatory compliance.
Monitoring and Response That Prevents Disasters
Even the most secure document management systems can be vulnerable. Continuous monitoring and a swift incident response are vital for true preparedness. This involves systems that detect suspicious activity before it escalates into a major breach.
Proactive Monitoring: Detecting Threats Early
Think of your document management system as a fortress. Strong walls (encryption) and guards (access control) are essential, but without constant surveillance, threats can penetrate. Proactive monitoring is your surveillance system, identifying unusual activity. This might include monitoring login attempts, file access, and permission changes. For example, multiple failed logins from an unknown location could indicate a brute-force attack. A sudden increase in downloads might signal unauthorized data exfiltration.
Audit Trails: Your Security Camera for Documents
For strong document management security and compliance, a solid data governance framework is beneficial. A helpful example can be found in this article about a data governance framework template. Comprehensive audit trails are also crucial. They provide a chronological record of all document activity: who accessed what, when, and from where. You might find this article helpful: How to master audit trail best practices. A robust audit trail not only helps identify breaches but provides insights for strengthening your security.
Incident Response: Containing the Damage
Even with proactive monitoring, breaches can occur. This is where a well-defined incident response plan is essential. A rapid response can minimize the impact of a breach. This involves isolating affected systems, identifying the breach's cause, and restoring data from backups. Like firefighters with procedures for extinguishing fires, a clear incident response plan guides organizations through containment and recovery.
Continuous Improvement: Learning from Incidents
Successful organizations use monitoring data to continuously improve their document security. Each incident becomes a learning opportunity to identify vulnerabilities and refine security measures. This continuous improvement cycle strengthens the system, making it more resilient to future threats. This constant evolution ensures your document management system is always improving.
Secure your valuable documents with Whisperit's advanced document management security features. Visit Whisperit today to learn more about protecting your business.