Cross Border Data Transfer: Essential Guide for Compliance
Think about sending a valuable package to another country. You wouldn't just drop it in the mail and hope for the best. You'd have to navigate customs, follow the destination country's rules, and make sure it's packed securely. Cross-border data transfer is the digital equivalent of that process, and it's happening all the time, whether we realize it or not.
What Is Cross Border Data Transfer, Really?
At its heart, cross-border data transfer is simply the electronic movement of personal or sensitive information from one country to another. As our world has become more connected, this practice has absolutely exploded. It’s no longer a niche activity; international data flows are the lifeblood of the global economy, allowing businesses to compete and innovate on a worldwide scale.
Of course, this explosion in data movement has created a tangled web of legal and technical hurdles. It's a complex topic, and you can get a deeper understanding of the challenges from this insightful article on captaincompliance.com.
Think of it as the engine powering our digital world. This isn't just something for massive tech giants to worry about; it's a daily reality for nearly any business with an online presence.
Everyday Scenarios of Data Transfer
Chances are, your business is engaged in cross-border data transfers without giving it a second thought. Here are a few common examples:
- Using cloud services: If you use a cloud platform like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud, and their servers aren't in your country, that's a cross-border transfer.
- Serving international customers: A small e-commerce shop in the U.S. that takes an order from someone in France is moving personal data across borders.
- Working with remote teams: A company with employees or contractors scattered across the globe constantly shares data internationally just to get work done.
This flow of information is critical for everything from managing customer relationships and analyzing business trends to handling basic back-office tasks.
To truly grasp the concept, it helps to break down the core components involved in any international data flow. Each piece has its own role and associated concerns that businesses must address.
Core Components of International Data Flow
| Component | Description | Primary Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Data Subject | The individual whose personal data is being collected or processed (e.g., a customer, employee). | Ensuring their privacy rights are protected regardless of where their data goes. |
| Data Controller | The organization that determines the "why" and "how" of data processing (e.g., your business). | Ultimate responsibility for compliance and lawful data handling. |
| Data Processor | A third-party organization that processes data on behalf of the controller (e.g., a cloud provider). | Ensuring they meet the controller's security and compliance requirements. |
| Transfer Mechanism | The legal framework that legitimizes the data transfer (e.g., Adequacy Decision, SCCs). | Finding a valid and legally sound basis for moving the data. |
| Jurisdictions | The countries the data is leaving (exporting) and entering (importing). | Navigating and reconciling the different, often conflicting, laws of each country. |
Understanding these individual parts is the first step toward seeing the bigger picture and managing your responsibilities effectively.
The key takeaway is that data rarely stays put. Its journey across geographical and legal boundaries requires careful management to ensure security and compliance with a patchwork of international regulations.
Without a clear map of how your data moves, you’re essentially flying blind. This can lead to serious compliance risks, steep fines, and significant damage to your company's reputation. Recognizing that every international email, customer interaction, and cloud backup is part of this global ecosystem is the foundation of a smart data governance strategy.
Decoding the Global Maze of Data Privacy Laws
Trying to navigate international data regulations can feel like trying to solve a puzzle where the pieces keep changing shape. Laws like the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) create a complex patchwork of rules that govern every single cross border data transfer.
These aren't just bureaucratic hurdles. They're built on the fundamental idea that a person's data belongs to them, and its protection should travel with it, no matter where in the world it goes. Because of this, a one-size-fits-all approach to compliance is a recipe for disaster. An action that's perfectly fine in one country could land you in serious trouble in another.
A World of Different Rules
The global regulatory scene is fragmented, and it’s always in flux. Each major economic power has carved out its own unique framework, which creates a real challenge for any business operating on the world stage.
- The European Union (GDPR): The GDPR really set the global standard. It puts a heavy emphasis on consent, data minimization, and the "right to be forgotten." Most importantly, it has an extraterritorial reach, which means it applies to any company in the world that handles the data of EU residents.
- The United States (Sector-Specific): The U.S. doesn't have one overarching federal privacy law. Instead, it’s a mosaic of federal and state-level rules. As of early 2024, over a dozen states—including California with its game-changing CCPA—have passed their own comprehensive privacy laws.
- China (PIPL): China’s PIPL is one of the strictest data privacy laws on the planet. It demands explicit consent for data collection and places tight restrictions on moving data outside of the country.
This variety means companies have to stay sharp and adaptable. Knowing the fine print for each region isn’t just a good idea—it’s absolutely critical for operating legally and keeping your customers' trust.
The common thread tying all these laws together is data sovereignty—the concept that data is governed by the laws of the nation where it was collected. Getting this right is the cornerstone of modern data privacy compliance.
Why Constant Vigilance Is Key
The legal ground under your feet is constantly shifting when it comes to cross border data transfers. Frameworks get updated, new court decisions set precedents, and geopolitical events can make once-reliable transfer methods obsolete overnight. This makes proactive compliance a core business function, not a one-time project.
As you work through this complex world, making sure your practices are fully aligned with every legal mandate is non-negotiable. Using a comprehensive business compliance checklist can be a great way to structure your efforts. But staying informed is only half the battle. The real work lies in implementing, documenting, and proving your adherence to these rules. If you're looking to dive deeper, our guide on building a solid data privacy compliance strategy is a great next step. This ongoing effort is what protects your organization from risk and builds a reputation as a company that truly respects privacy.
Understanding the Physical Journey of Your Data

It’s easy to think of data as something that just vanishes and instantly reappears on the other side of the world. But every single cross border data transfer is a very real, physical journey. Your information travels through a massive network of undersea fiber-optic cables, land-based networks, and sprawling data centers. The physical route is just as critical as the digital encryption protecting it.
Think of it this way: the legal rules are like customs regulations for a package, but the physical infrastructure is the actual shipping route. The path your data takes—and the "ports" it stops at along the way—has a direct impact on everything from speed and performance to your exposure to security and legal risks. Picking a cloud provider or data center location isn't just a technical choice; it's a strategic move with huge compliance implications.
The Impact of Infrastructure on Compliance
The physical location where your data is stored determines which country’s laws govern it. This principle, known as data residency, is a cornerstone of modern data privacy. If your business is based in Canada but you use a cloud service with servers in the United States, your data falls under the jurisdiction of U.S. law enforcement and surveillance programs.
This reality has kicked off a major global trend toward data localization. Many countries now insist that specific types of data must be kept within their own borders. This is a direct response to the fact that the world's data centers are far from evenly distributed. The United States, for instance, is home to nearly 46% of the world's data centers, while entire continents have only a tiny fraction of that capacity. This imbalance makes many governments nervous.
Understanding your data's physical path is as critical as securing the data itself. The location of the servers holding your information dictates the legal jurisdiction, security standards, and potential access rights of foreign governments.
Emerging Markets and Strategic Placement
To tackle this imbalance and provide better service, infrastructure is finally expanding into new regions. This is particularly true in major emerging markets, where rapid digitalization is creating immense demand for local data processing.
Take a country like India. Expanding its data center footprint is essential for managing the explosion in internet usage, especially in smaller Tier-II and Tier-III cities. These locations offer lower costs and allow data centers to be built closer to the people who actually use the services. This strategic placement cuts down on latency, speeds everything up, and is vital for efficiently managing both local and international data flows. To get a sense of how this is shaping policy, you can explore the recommendations on India's digital infrastructure.
By placing infrastructure strategically in these growing areas, companies can boost performance and help close the digital divide. It gives local businesses the foundation they need to compete on a global scale while offering international firms a compliant way to enter new markets. This is why the physical location of your data is a central piece of any smart cross border data transfer strategy.
Choosing the Right Tools for Lawful Data Transfers
Navigating the legal maze of a cross-border data transfer isn't just about knowing the rules; it's about having the right tools in your toolkit. Think of these tools as different legal passports for your data, each designed for a specific kind of international journey. Picking the right one is a crucial step to keep your global operations both secure and on the right side of the law.
The three main mechanisms you'll encounter are Adequacy Decisions, Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), and Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs). Each has a specific job, and understanding which to use—and when—can be the difference between smooth sailing and a massive compliance headache.
The Easiest Path: Adequacy Decisions
The most straightforward route for transferring data is when the destination country has an adequacy decision. This is basically a stamp of approval from a regulatory body, like the European Commission, certifying that a country's data protection standards are just as strong as their own.
When an adequacy decision exists, data can move to that country without any extra paperwork or safeguards. For instance, the EU considers countries like Switzerland, Canada, and Japan to have adequate data protection laws. It's the simplest path, but it's only available for a select list of approved nations.
The Most Common Tool: Standard Contractual Clauses
So what do you do when there's no adequacy decision? You turn to the most common tool in the box: Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs). These are pre-approved, standardized legal contracts that both the data exporter and importer sign. They establish a formal agreement to protect the data according to the rules of the exporting country’s laws, like the GDPR.
SCCs are incredibly versatile and practical. A small business in Spain that uses a US-based cloud service, for example, would almost certainly use SCCs to make that data flow legal. They are the workhorse for most business-to-business relationships involving international data, forming the legal backbone for millions of organizations. A huge piece of this puzzle is ensuring the data is technically secure while it's moving, which is where a solid solution for encrypted file transfer is absolutely essential.
The Corporate Framework: Binding Corporate Rules
For large, multinational corporations, there’s another path: Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs). These are a company's own internal data protection policies that have been formally approved by a data protection authority. BCRs give a corporate group a green light to transfer personal data internationally between its own companies, offices, and subsidiaries without needing to sign new SCCs for every transfer.
BCRs are like an internal company passport for data. Once approved, they streamline the cross border data transfer process within the corporate family, making them ideal for global enterprises that frequently move information between international offices and subsidiaries.
To keep operations running smoothly and manage these complex regulations, many businesses find that looking into compliance automation software provides a significant advantage.
This decision tree gives you a visual guide to the key checkpoints for a compliant cross-border data transfer, walking through destination, encryption, and regulatory review.
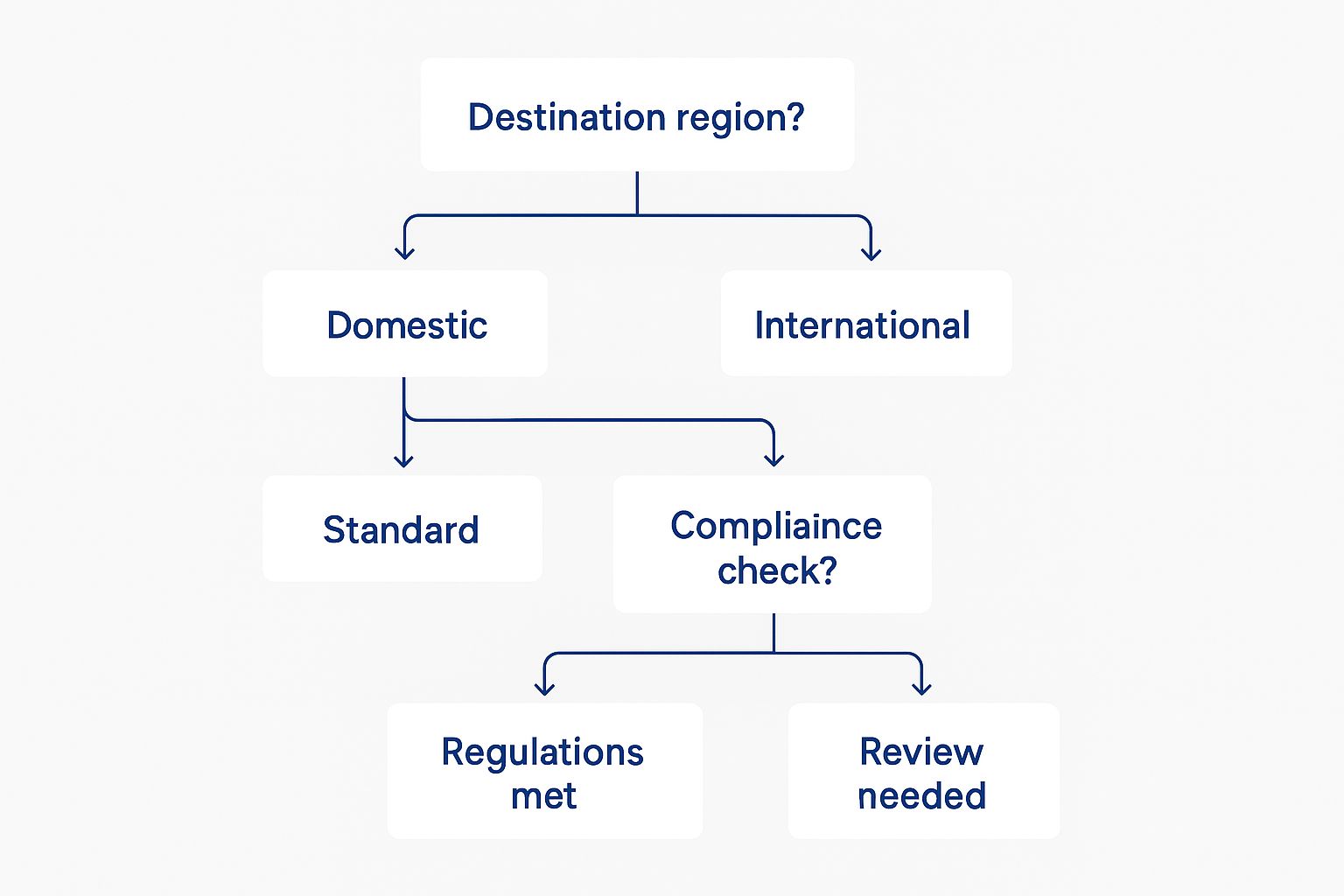
The key takeaway here is that every single international transfer demands a careful look at the destination's legal landscape and the implementation of the right safeguards to protect the data.
Building Your Data Transfer Risk Management Plan

Knowing the rules and having the right tools for a cross border data transfer is one thing, but that knowledge doesn't do much on its own. The real work begins when you build a proactive risk management plan. This is where you turn abstract legal requirements into concrete, everyday actions, shifting compliance from a chore into a genuine business advantage.
A solid plan doesn’t just wait for problems to pop up; it gets ahead of them. It starts with creating a crystal-clear picture of how your information flows, spotting potential weak spots long before they can be exploited. This proactive approach is what separates companies that just check boxes from those that truly safeguard their data.
Begin with Comprehensive Data Mapping
Let's be blunt: you can't protect what you don't know you have. The first, and most important, step is data mapping. This is all about creating a detailed inventory of every piece of data your organization holds. You need to document what you collect, where you keep it, who can access it, and—crucially for our topic—where it goes.
Think of it like drawing a supply chain map, but for your data. This map becomes your definitive guide, showing every single point a cross border data transfer happens, whether it’s moving to a cloud server, a software vendor, or one of your own international offices. Without a clear map, you're flying blind.
A thorough risk management plan moves beyond just technical safeguards. It involves a holistic view of your data's lifecycle, from creation to transfer, ensuring every step is assessed for legal, operational, and security risks.
Conduct a Transfer Impact Assessment
Once you know where your data is headed, you have to figure out the risks of sending it there. This is done with a Transfer Impact Assessment (TIA), which you might also see called a Transfer Risk Assessment (TRA). A TIA is basically a formal, documented evaluation of the legal and practical risks tied to a specific data transfer.
This assessment forces you to ask some pointed questions:
- Legal Protections: Does the destination country have laws that protect data as well as your home country does? Is there a risk of government agencies getting access to the data without proper checks and balances?
- Security Measures: What technical and organizational safeguards are in place while the data is moving and after it arrives? We’re talking about things like encryption, access controls, and security protocols.
- Vendor Reliability: How trustworthy is the third party on the receiving end? This question connects directly to your broader third-party risk strategy. For a closer look at this, our guide on effective vendor risk management is a great resource.
Implement Crucial Security Measures
The insights from your data map and TIAs will tell you exactly where to focus your security efforts. Armed with this knowledge, you can put targeted measures in place to protect your data where it’s most vulnerable.
Key security controls you'll want to consider are:
- End-to-End Encryption: This is non-negotiable. Data must be unreadable both on its journey (in transit) and when it’s stored (at rest), making it useless to anyone who might intercept it.
- Data Minimization: A simple but powerful principle: only send the absolute minimum amount of data required for the job. If you don't need a specific piece of personal info, don't include it in the transfer.
- Strict Access Controls: Put policies in place that ensure only authorized people can touch the data. This is often called the principle of least privilege, and it’s a cornerstone of good security.
By systematically mapping your data flows, assessing the risks, and putting the right protections in place, you build a resilient risk management plan. It’s a plan that not only satisfies regulators but also builds lasting trust with your customers and partners around the world.
How Secure Platforms Make Global Compliance Possible
When it comes to managing cross-border data transfer, technology isn't just part of the solution—it's the bedrock of your entire compliance strategy. Relying on the right secure platform can transform the headache of navigating international regulations into a manageable, almost seamless process.
It’s about moving from a reactive stance to a proactive one. Instead of scrambling to meet compliance demands after the fact, a well-built platform bakes compliance right into your day-to-day operations. Think of it as translating dense legal jargon into automated, invisible guardrails that protect your data without slowing you down. This frees up your teams from the immense burden of manual oversight and lets them focus on what they do best.
Turning Technical Features into Trust
A truly secure platform isn't just about a long list of tech specs; it's about how those features solve real-world problems. The goal is to build an environment where compliance is the default setting, not a box to be checked later.
Here’s how specific technologies directly address the challenges of moving data across borders:
- End-to-End Encryption: This is your data's first line of defense. It ensures that from the moment a file is sent to the second it’s opened, it's completely unreadable to anyone without the key. It's a non-negotiable for meeting GDPR standards and protecting information while it's on the move.
- Secure Enclaves: Imagine a locked, soundproof room inside a secure facility. That's what a secure enclave is for your data. It processes information in a completely isolated environment, meaning not even the platform provider can peek at the raw data. This adds a powerful layer of protection that significantly bolsters your Transfer Impact Assessments (TIAs).
- Strict Access Controls: This is about enforcing the "need-to-know" principle. These controls guarantee that only the right people can access sensitive information, and only when they absolutely need to. For regulators, this is crucial proof that you are in full control of your data.
When a platform combines these elements, it does more than just protect data—it builds a clear, auditable trail of your commitment to privacy.
Technology is what bridges the gap between regulatory theory and business reality. A secure platform doesn't just lock down data; it simplifies GDPR compliance, cuts down on risk, and gives you the confidence to operate anywhere in the world.
This integrated approach is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity for modern business. A well-designed platform automates the critical checks and balances, dramatically reducing the chance of human error and eye-watering fines. To better understand how to evaluate these dangers, you can learn more about conducting a thorough security risk assessment in our guide.
Platforms like Whisperit were built from the ground up for this very purpose, using Swiss hosting and powerful encryption to ensure your most critical information stays protected, no matter where it's headed.
Answering Your Questions on Cross-Border Data Transfer
Even with a good grasp of the basics, some practical questions always pop up when it's time to put theory into practice. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to clear up any lingering confusion.
What’s the Biggest Mistake Companies Make?
By far, the most common pitfall is treating compliance like a one-and-done project. It's easy to think you can set everything up, check a few boxes, and be done with it. But that's a recipe for trouble.
Data privacy isn't static. New laws are passed, existing ones get updated, and court rulings constantly redefine the rules. Thinking of this as a "set it and forget it" task is the fastest way to find yourself non-compliant. Real data governance is an ongoing commitment, a living process that adapts as the world changes.
Is My Small Business Exempt From These Rules?
This is a frequent question, and the answer is almost always no. Regulations like the GDPR don't really care about how big your company is; they care about whose data you're handling. If you have customers, clients, or even just website visitors from the European Union, you're on the hook.
While your company's size might change the scale of what you need to do, it almost never gives you a free pass. Any business that deals with personal data from other countries needs a solid plan for transferring it lawfully.
The core idea to remember is this: a person's privacy rights travel with their data. If you handle data from a protected region, you have to play by their rules, no matter where your office is located or how many employees you have.
How Often Should We Review Our Data Transfer Practices?
As a rule of thumb, a deep dive into your data transfer policies and safeguards should happen at least annually. But that's just the baseline. Certain events should trigger an immediate review.
It’s time to reassess your setup whenever:
- You bring on a new international vendor or partner.
- You start marketing or selling to customers in a new country.
- A major privacy law (like a new state law or an update to GDPR) is passed or changed.
Think of it as part of your regular operational hygiene. A great way to start is by weaving these checks into your existing security procedures, much like you would follow a detailed security audit checklist.
Ready to secure your global communications? Whisperit provides end-to-end encrypted solutions with Swiss hosting to ensure your sensitive information remains protected, no matter where it goes. Discover secure, compliant data handling at https://whisperit.ai.